Best GIS Software for 2020
Last Updated on - The GIS software (geographic information system) allows you to create maps and other graphic displays of geographic information for analysis and demonstration. With these abilities, a GIS is an important tool to visualize spatial data or to build decision support systems for use in your organization. GIS data help us in understanding and meeting global challenges. As GIS technology quickly advances, there are various pioneering applications in the planning sector. GIS software can be used to integrate geographic intelligence into planning processes and can change how we think and behave. The major function of GIS software is to provide a visual representation of data. It is projected that 80% of the data we consider has a geospatial element of some form. The GIS software (geographic information system) provides a source for that data to be stored in a database and then represented visually in a mapped format.Top 10 GIS Software (geographic information system)
- Hexagon AB GIS Software
- Environmental Systems Research Institute Inc
- Trimble Inc GIS Software
- Pitney Bowes GIS Software
- Bentley GIS software
- GE GIS Software
- Topcon Corporation
- Autodesk Inc GIS Software
- Computer Aided Development Corporation Limited (Cadcorp)
- Pasco Corporation
GeoMedia - GeoMedia, by Hexagon, is an impressive, flexible GIS management platform that allows you to aggregate data from a variety of sources and analyze them in unison to extract clear, actionable information. GeoMedia’s ability makes it perfect for extracting information from a collection of dynamically changing data to support informed, smarter decision-making. Read more
ArcGIS Online - ArcGIS Online, part of the Esri Geospatial Cloud permits you to connect people, locations, and data with interactive maps. The GIS software enables us to work with smart, data-driven styles and instinctive analysis tools that deliver location intelligence. It also allows you to share your insights with the world or specific groups. Read more
TerraSync GIS Software - TerraSync Software by Trimble is intended for fast and efficient field GIS data collection and maintenance. It is simple and easy to use, efficient, and highly productive in the field, that makes TerraSync perfect GIS software solution is for collecting and maintaining high-quality GIS data. Read more
MapInfo Pro GIS software- MapInfo Pro, by Pitney Bowes, enables you to explore, model, and act with confidence on site selection, asset management, demand generation, and risk management/service resource allocation. The GIS software also helps you to create a model of your world so that you can simulate different alternatives to guide your actions. Read more
Bentley GIS ssoftware - Bentley GIS software allow you to map, manage, analyze, view, and understand the infrastructure around you, no matter what your level of GIS experience. It helps to improve association on multi-discipline projects by leveraging the strengths of both CAD and GIS. The GIS software also enables us to make better, quicker decisions and support planning, design, and geospatial information management in one powerful 2D/3D GIS. Read more
GE Smallworld GIS software- GE Smallworld provides the basis to manage the lifecycle of network assets, where geospatial data is a crucial role in satisfying business-critical processes. The GIS software is capable to integrate with other products that require spatial information, including systems for customer relationship management, market analysis, network, and work management. Read more
MAGNET Field GIS software- MAGNET Field GIS, by Topcon, is a powerful and instinctive field application software that will enhance your GIS productivity and allows you to connect in the field as well as in the office. IT offers graphical icons and intuitive workflows that help accomplish GIS field tasks such as collection, navigation, data update, code libraries, and measurements. Read more
AutoCAD Map 3D - AutoCAD Map 3D GIS software provides access to GIS and mapping information to support design, planning, and data management. The GIS software also provides Intelligent models and CAD tools that help you to apply regional and discipline-specific standards. With the integration of GIS data, it helps to improve quality, productivity, and asset management. Read more
Market Overview
The global geographic information systems (GIS) market size is projected to grow from USD 8.1 billion in 2020 to USD 14.5 billion by 2025 at a CAGR of 12.4% from 2020 to 2025. Expansion of smart cities and urbanization, integration of geospatial technology with majority technologies for business intelligence, increasing investments in modern GIS software, and growing accessibility of spatial data and cloud technology are some of the key factors driving the growth of the GIS software market. Moreover, in recent years, cloud computing has created opportunities for GIS to efficiently deliver geographic information and reduce the cost incurred in designing, building, deploying, and supporting these services. Additionally, the development of 4D GIS software is looked at as a major growth opportunity for the GIS Software market.
GIS software (geographic information system) captures, stores, manipulates, analyzes, manages, and displays spatial or geographic data on a map. GIS software also allows the users to create interactive queries, analyze the spatial information, edit data on maps, and present the results of these operations on devices such as desktop, mobile, and tablets. The GIS software creates a large amount of data, combining different layers of information to manage and retrieve the data in a more useful manner for almost every industry. Geographic information system (GIS software) is an electronic information system that analyzes, integrates, and displays information based on geographic locations.
GIS software provides a visual representation of geographic analysis on maps. Geospatial technology is used to acquire, manipulate, and store geographic information. The growth of the GIS software market is driven by the development of smart cities and urbanization, integration of geospatial technology with mainstream technologies for business intelligence, and growing adoption of GIS software in the transportation sector. This market holds several opportunities for existing and entry-level companies to enable them to expand their businesses.
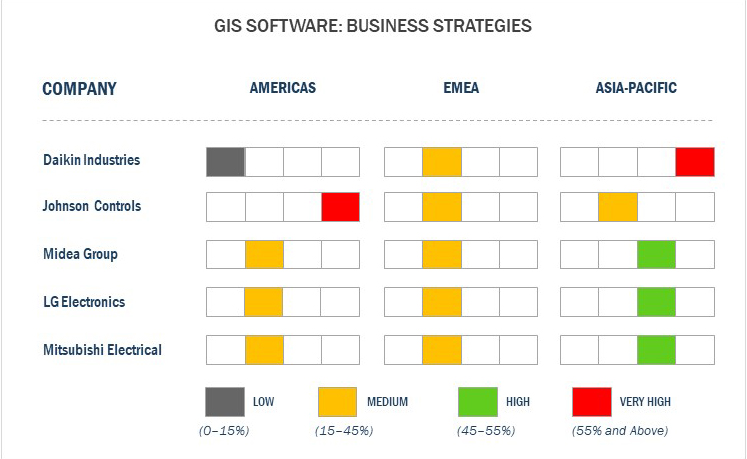
The MicroQuadrant matrix provides information about the GIS Software companies. It outlines the findings and analysis of how well each market vendor performs within the predefined MicroQuadrant criteria. The vendor evaluations are based on 2 broad categories: strength of product portfolio and business strategy excellence. Each category carries various criteria, based on which the vendors have been evaluated. The evaluation criteria considered under the strength of product portfolio include breadth and depth of product offering (based on the industries that the vendors cater to and their GIS and service offerings), product feature and functionality, focus on product innovation, and product quality, reliability, and support focus on product innovation. The evaluation criteria considered under the business strategy excellence include the geographic footprint (based on geographic presence), vision alignment, breadth of application served and coverage, channel strategy and fit, and mergers and acquisitions strategy.
Autodesk, Inc., Bentley System Incorporated, Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc. (Esri), General Electric Co., Hexagon AB, Pitney Bowes Inc., Topcon Corporation, and Trimble Inc. has been recognized as the visionary leaders in the GIS market. They offer a strong portfolio of solutions and services to their commercial clients. The products and solutions of these companies are highly scalable and can be customized as per the requirements of the clients. These companies are said to be investing significantly in R&D to introduce innovations in location-based services and GIS. Moreover, these companies have also undertaken various organic and inorganic strategies to achieve consistent and advanced growth in the best GIS software market.
Blue Marble Geographics, Caliper Corporation, Computer Aided Development Corporation Limited (Cadcorp), Geosoft Inc., Handheld Group AB, Harris Corporation, Hi-Target Surveying Instrument Co., Ltd., MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates Ltd., and Pasco Corporation have been recognized as the dynamic differentiators in the GIS software industry. These companies have a significant network of channel partners and resellers to increase the deployment of their solutions across a multitude of verticals. The dynamic vendors have been consistently generating positive revenue growth in the GIS Software market and their market position has heightened by their organic and inorganic ventures.
AmigoCloud, Inc., Takor Group Ltd., and Maptoss Technologies Pvt. Ltd. have been recognized as innovators in the GIS software industry. These companies offer innovative solutions for fixed and mobile GIS Systems. They also have a strong breadth and depth of product offerings. The innovators have been at the forefront in deploying their solutions for niche and custom software requirements of the clients.
Manifold GIS Software Limited, Beijing Unistrong Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Champion Instruments, LLC, Golden Software LLC, and SuperMap GIS Software Co., Ltd. have been recognized as the emerging companies in the GIS Software market. The emerging players are specialized in offering highly niche and tailor-made GIS solutions and services to their clients. These companies devise new ways of working to drive business results in the market.
Major Business Strategies adopted in the GIS market
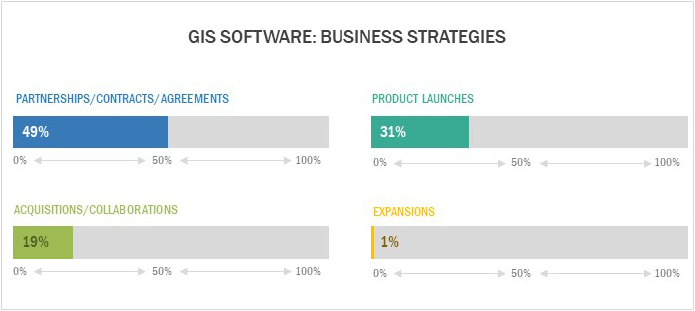
Business Strategies adopted by key Vendors in GIS market
GIS Software- Market Dynamics
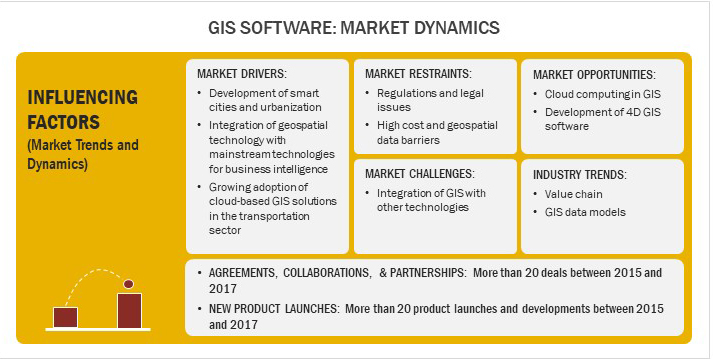
What are the major drivers in the GIS Market?
Development of smart cities and urbanization
The process of urban development demands a quick response and a topographical view of cities and towns. Consequently, it is essential for the government to integrate GIS software into urban planning and management. Remote sensing GIS is helpful for surveillance and measurement of objects from a distance, i.e., instruments or recorders are not in direct connection with objects under exploration. Smart city planning needs a large volume of data both at the time of planning and at the time of execution of the plan to decide the status of the available abilities. For a smart city, it would be essential to use GIS solutions for land use management to keep track of zoning and related data of buildings and occupancy. the GIS software provides precise, orderly, and reliable information for the planning and management of a smart city. GIS Software is increasingly being used in the construction of smart infrastructure planning and green buildings as GIS easily interfaces with building information modeling (BIM). Some of the application areas of GIS in smart city development include smart urban planning, smart utilities, and smart public works. For the expansion of smart cities, GIS spatial analysis tools are used for effective decision-making for urban growth management. GIS remote sensing systems are very useful for change detection analysis and selection of sites for facilities such as restaurants, hospitals, and solid waste disposal.
Integration of geospatial technology with majority technologies for business intelligence
Convergence and incorporation of geospatial technology with majority technologies such as analytical tools, database, & enterprise solutions (e.g., ERP and CRM) are considered one of the crucial drivers expanding the utility of geospatial analytics across various industries. Geospatial data collected from several sources are stored, processed, and analyzed to derive geographic information. The geospatial analyzed data is used for better decision-making by various end-users. The acceptance of geospatial technology has further resulted in enhanced productivity and efficiency of enterprises across different sectors such as telecommunication, construction, agriculture, transportation, energy, mining, oil & gas, and business enterprises. For example, real estate site selection, route selection, zoning, planning, conservation, and natural resource extraction include the usage of geospatial analytics and GIS software. Geospatial software and service providers can deploy more complete solutions through technology convergence and incorporation with majority technologies. Therefore, the integration of geospatial technology with majority technologies for business intelligence is one of the key drivers for the growth of the GIS software market.
Rising adoption of GIS in the transportation sector
GIS Software is useful in transportation planning agencies, especially among urban transportation organizations. In many advanced countries, highway maintenance management is becoming a serious issue. Many authorities are using GIS for highways and transport management for storing and evaluating data on population densities, land uses and travel behaviors. Extensive adoption of GIS software for transportation applications such as highway maintenance, traffic modeling, accident analysis, and route planning is driving the market growth. GIS software is an influential tool in the analysis and design of transport routing networks. GIS for Transportation (GIS-T) have been widely adopted in transportation applications. Companies are focusing on developing the specific software solutions for the transportation sector. For example, Caliper Corporation (US) offers the TransCAD Transportation Planning Software specifically for use in the transportation sector to store, display, manage, and analyze transportation data.
GIS Software- Market Opportunities

GIS Software- Market Segmentation
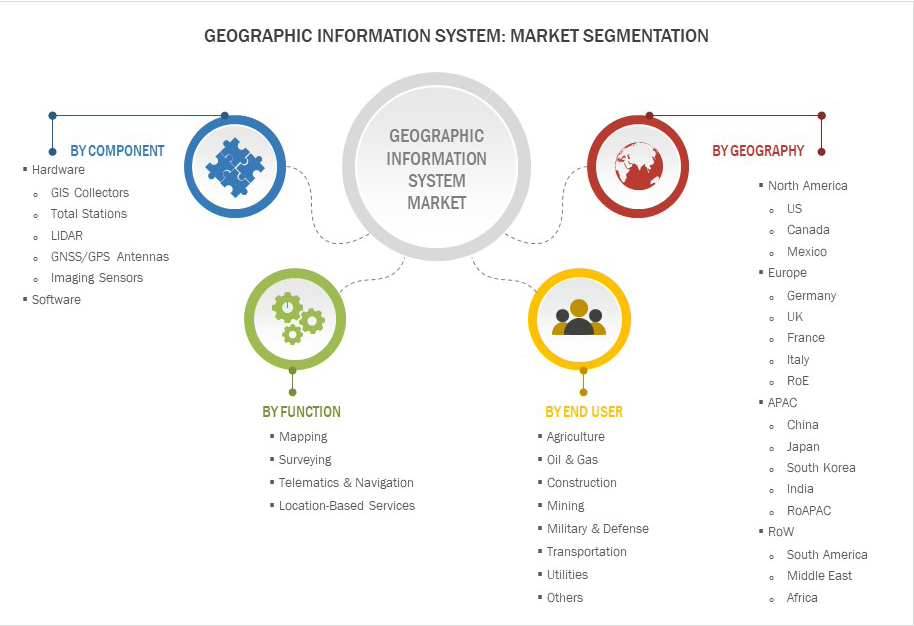
What are the major applications of GIS Software?
Agriculture
In agriculture, GIS software is used for a survey of plantation crops and the management of fertilizers, pesticides, and insecticides. The GIS Software is an important tool for mapping and managing agricultural resources as it provides analytics and supports users in decision-making for crop planning and land resource management. GIS plays a critical role in agriculture by growing yields, managing agricultural resources, forecasting outcomes of yield, and refining farm practices. Agricultural land mapping plays a significant role in the management of land resources. High-resolution geospatial images collected from remote sensing and land surveying are used to map and analyze soil data to develop farming methods and procedures. The use of GIS software in agriculture helps farmers to manage their land resources efficiently. Additionally, GIS technologies offer agricultural land cover mapping and valuation of crop damage caused by natural disasters.
Precision Farming
The farming industry has been accepting precision farming solutions at a quick pace. Several geospatial technologies such as remote sensing, GIS, and GPS are applied to observe various farm-field conditions and to analyze and forecast results. GIS plays a major role in precision farming applications such as landscape management, crop protection management, crop management, soil management, and waste and pollution management. Most of the precision agriculture activities rely on image-based data. GIS software is used to develop digital maps by converting spatial information collected through remote sensing or land surveying. Embracing LIDAR and other GIS technologies for precision farming has generated a significant opportunity in the GIS software market.
Oil & Gas
GIS plays a major role in the oil & gas industry. Crude oil and gas are generally found in deeper layers of the earth’s crust and hence it is essential to use precise technologies such as GIS for oil and gas exploration as well as for its suitable utilization. In oil & gas, GIS technologies such as satellite imagery and airborne remote sensing are broadly used for exploring oil & gas, drilling oil wells, and pipeline management. The GIS software offers insight on the selection of suitable areas for an exploration, drilling process. Exploration drilling and pipeline management need precise geographical data mapping. Additionally, GIS helps in locating new oil and gas resources and manage its extraction and supply.
Construction
The construction sector is a leading adopter of geospatial technologies. GIS has a significant role in mapping and surveying construction sites and serves as a comprehensive platform for the infrastructure development life cycle. Town planning and infrastructure development require accurate mapping and surveying of the geographic area. GIS software can precisely assess construction projects such as a dam, sewer, canal, industrial park, bridge, water management, and power plant. GIS software can be integrated with computer-aided design (CAD) tools for civil engineering applications. The growing urbanization and rising population have created an urge for the use of GIS for systematic and coordinated planning of land and other resources. Some of the major applications of GIS in construction are land surveying, urban planning, building information modeling (BIM), land cover mapping, property assessment, and smart city planning.
Mining
GIS technologies are used in mining for mineral exploration, mine planning, manufacturing plant setup, and infrastructural development. GIS is an ideal solution for analyzing various exploration data sets such as geologic maps, radiometric surveys, and mineral deposits. GIS software is used in mining processes to find the location for the construction of drifts, crosscuts, sublevels, manways, and ventilation shafts. Implementation of GIS in mining helps professionals to perform a detailed analysis of the geographic area and get an understanding of mining data to make decisions. In addition, with the use of GIS, users can overlay and analyze overlay interdisciplinary data such as geological maps, geophysical images, drill hole data, and information of core mineral resources. GIS analytics provide an analysis of the environmental impact of mining and manufacturing projects. GIS analytics is used to manage the extraction of natural resources such as petrol and natural gas.
Transportation
GIS Software is been rapidly used in transportation applications such as transportation planning, accident analysis, route planning. highway maintenance, and traffic modelling. With the help of GIS software, transportation planners can store and analyze geospatial data as well as mapping of transportation features with a base map. GIS has a crucial role in highway infrastructure management and the development of roads, railway routes, and bridges. With the rise in urbanization, there is a need for effective transportation planning. GIS software can be used in managing, planning, and analyzing transportation management systems. A combination of transportation information system (TIS) with GIS is commonly mentioned as GIS for transportation (GIS-T). With the rising adoption of GIS in transportation, companies are concentrating on developing transportation-specific GIS applications. For example, Caliper Corporation provides TransCAD, GIS, specially designed for transportation applications such as transportation planning, and traffic modeling.
Utilities
The management of utilities is the basic requirement for the efficient management of infrastructure. GIS-based utility mapping is used for mapping and modeling of utility management. Utilities are using geospatial technologies to assist in the setup of smart grids, asset management, and identify the damage or connectivity issues in pipelines as well as analyze underground electric wire damages. In the utility sector, GIS is widely used by electric, gas, and water and wastewater organizations for resource management. GIS is also used in environmental monitoring and disaster management applications.
a) Asset Management
Asset management is one of the important applications of GIS in the utility sector. GIS software is used for mapping and monitoring of utility assets such as wastewater and pipeline management. Accurate location data is required for water and wastewater management. GIS technologies are gaining traction as these offer accurate data and are feasible to implement for utility asset management.
b) Environmental Monitoring
Imagery data collected from various mediums are used to visualize and analyze the geographic as well as man-made features of a region to detect and monitor environmental changes. The GIS software provides integration, analysis, and map production to assess and monitor the environment. Global warming, as well as increasing population and food and water scarcity, have led governments across the world to closely monitor environmental changes using GIS analytics solutions. For example, in 2017, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) signed a contract with Woolpert, Inc. (US). With this contract, Woolpert will supply GIS, remote sensing, and related consulting services to EPA.
c) Disaster Management
GIS has emerged as a decision support tool for disaster management. GIS helps users by providing a better geographic view to take the most appropriate decision in handling a disaster or to plan for tackling natural disasters. The GIS software is used in disaster management applications such as early warning systems, pre-disaster planning, damage assessment, and relief management.
d) Grid Management
Grid management is evolving as a major application of GIS in utilities. Increasing adoption of GIS in smart grid management for applications such as distribution management system (DMS), energy management system (EMS), outage management system (OMS), and mobile workflow management (MWFM) is driving the GIS market in utilities. Smart grid management largely depends on geographic data. GIS allows the user to monitor grid locations and real-time status of the fieldwork. With the use of GIS, users can quickly monitor smart grid activities.
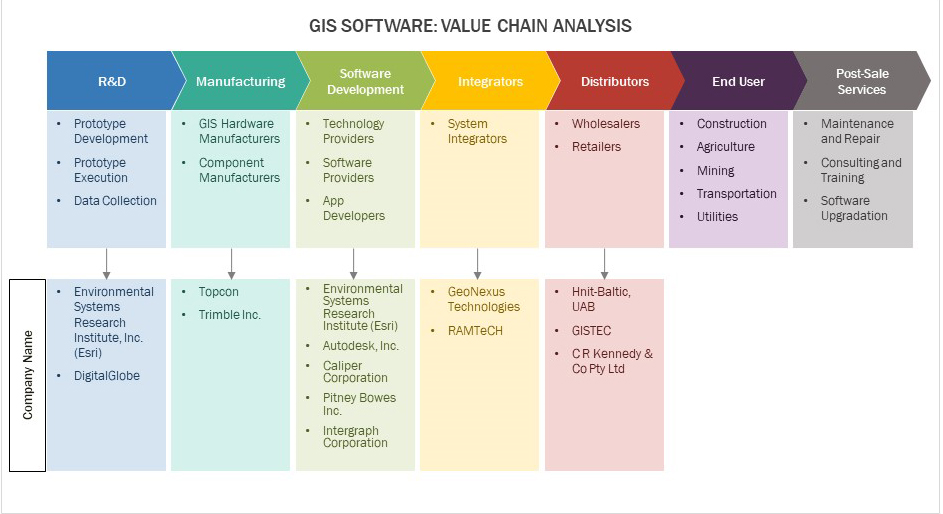
GIS Software - Value Chain Analysis
What are the key GIS Software features?
Map Creation & Publishing
Map creation is one of the crucial features while selecting the GIS software, one should evaluate the limitations of map creation tools. There are many map makers that only permit you to use land and topographical features already provided by external map sources. Others can’t import these, which means that must reproduce the shape and features for accuracy.
A proper map application has functions for importing existing data of all types from external sources but also permits you the finalize shaping and laying things out. Geospatial information, latitude and longitude coordinates, visual shaping and object placement tools, and the proper assignment of analytics can be used to locations, regions, or other such things. This enables you to create complete maps with things marked out and coded to match statistics based on your geospatial analytics. This provides a very visual, very instinctive way to present this information to people, escaping the bonds of jargon and specialty knowledge altogether.
Spatial Analysis
It’s good to have various statistical things to be presented in a visual way, but without built-in functions to do these calculations, it becomes difficult to achieve your goal. Therefore, the top GIS mapping technologies have several ways to set up interrelationships, scales, gradients, and much more, to provide true, accurate, complete spatial analysis based on real map data. This helps further to derive graphs, charts, and projections from these, and from comparisons of various per-region calculations. This helps in understanding better customer relationship management (CRM), where you can better manage people based on their location. It also enables for shorter hold times by classifying your help staff into regions, if you have the workforce to support this.
Geocoding
Geocoding, an important software feature is a process of converting a street address into longitude and latitude coordinates. Geocoding and reverse geocoding are used frequently by software giants like Google or Apple Maps, providing address-based locations on a map, followed by a more fixed, accurate location based on geocoding and reverse geocoding to make these two locational sets identical.
This helps to better identify the location of a caller based on some slightly purposely inaccurate locational data from the phone itself. This could be a slippery slope, as it’s identical to making an intentionally slightly blind tracking device, but this has potential for rescue, police, and possibly for enterprises that do deliveries via mail or in person. This will also further help in enhancing GPS as time goes by.
What are the different functions of GIS Software?
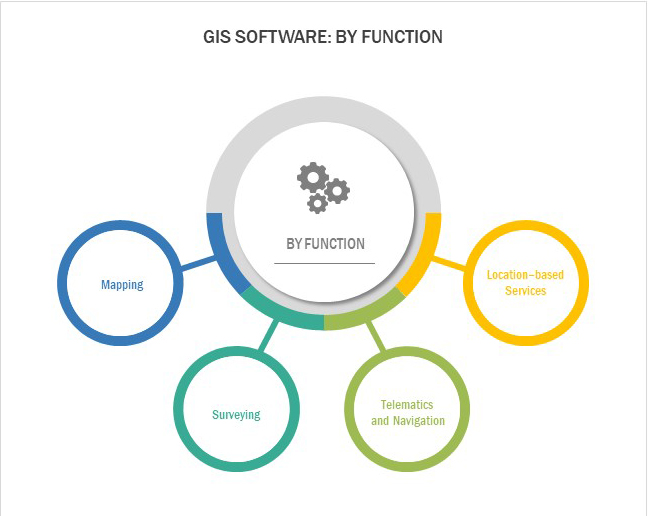
Mapping
Mapping function largely includes cartography, i.e., the designing of maps by representing important topographies of the earth’s surface with a symbolic representation. Mapping involves plotting the location of various altitude values on a base map. Technologies such as remote sensing, UAVs, LIDAR, and image sensing are widely used to collect data required for mapping and monitoring purposes. Remote sensing and LIDAR have the potential to drive the GIS market as these technologies provide more accurate data mapping over the traditional photogrammetry techniques. GIS software is an effective tool for geological mapping. It allows the user to view 2D and 3D representation of a geographic area with high precision. Mapping is used to visualize GIS data stored in GIS databases. Some of the mapping applications of GIS include soil mapping, regional planning, wetland mapping, coastal zone mapping, forest fire hazard zone mapping, and geologic mapping.
Surveying
Surveying is a technique to determine the distance and angles between two points on the earth’s surface. Surveying plays a central role in a wide range of applications such as infrastructure development, transportation planning, land boundary determination, construction planning, urban planning, and smart city development. Surveyors use GNSS hardware and GIS software to collect, import, convert, and store geographic data. Devices such as robotic total stations, GNSS receivers, GIS collectors, and handheld tablets are mainly used for land surveying. Remote sensing technologies such as satellite imagery and LIDAR are widely used for aerial surveying to collect and monitor the data. GIS software is used to incorporate, modify, and analyze the surveying data. GIS provides functionality to conduct spatial analysis, overlay data, and integrate other solutions with existing geographical data. GIS software is used for surveying in utilities, construction, mining, oil & gas, transportation, agriculture, and another end-user
Telematics and Navigation
The telematics and navigation function provide real-time geographic information on devices such as navigation systems and mobile devices. Telematics and the navigation function is mostly transportation for fleet management. Fleet management uses telematics and navigation to manage monitor commercial vehicle operation, location, and status. It allows the user to visualize display directions on the map with instructions for navigation, physical distance, and traffic.
Vehicle and traffic management require real-time data processing environment for processing traffic-related data. GIS-assisted telematics function provides collection, evaluation, and visualization data and helps the user in vehicle routing, route planning, and transportation management. systems offering telematics and navigation functions are used in conjunction with GPS technologies. the advent of the intelligent transportation system (ITS) and intelligent vehicle highway system (IVHS), an increase in the adoption of GIS-based telematics and navigation services. The development of transportation technologies such as connected vehicles and automated vehicles has contributed to ever-increasing demand for GIS-based telematics and navigation services. Telematics and navigation increasingly used in the management and analysis of shipping and marine transport processes.
Location-based Services
Location-based service (LBS) is the ability of the GIS to accurately guide the user using a mobile device to nearby places of interest. LBS is an evolving technology that provides real-time spatial information through mobile and field devices. Internet GIS and mobile GIS are significant LBS applications, as these provide exact positioning and real-time information through mobile-networked environments. GIS-based LBS provides real-time information such as real-time traffic conditions, emergency services, city routes, point of interest (POI), and public transport schedules. The quick evolution of smartphones and the accessibility of fast wireless internet connectivity is further projected to drive the growth of the LBS function during the forecast period.
What are the major benefits of GIS Software?
Make Better Business Decisions
Companies can gain critical ideas by integrating regional and location-related information with other company information that helps their businesses succeed. With spatial issues, companies can select trading places, assistance areas and clients of interest, and existing the details in thematic maps and reviews to achieve quicker and better company choices.
Enhance Functional Performance & Reduce Cost
The facts provided by GIS is used to greatly enhance operational preparing and control, and to re-engineer and expand company procedures. It offers you solutions for redirecting optimization and servicing preparing and confirming.
Improve Customer Service and Increase Sales
Understanding your clients, providing them with the greatest possible support, and finding more people like them is core to increasing revenue. GIS helps businesses to recognize their clients and use spatial issues to determine regional areas where similar census applies to focus on industry development.
Better & More Cost-effective Plan Citizens
Government authorities, especially municipal corporations, face remarkable difficulties in the economy. They have to face providing increasing communities, with higher objectives of support, while dealing with reducing sources. GIS provides an efficient remedy to improving vital resident services such as to permit/licensing, preparing, servicing, features control, and trains and buses.
What are the Current Trends in the GIS Software Market?
The potential to create small and often inexpensive devices and sensors with wireless connectivity is driving an explosion of the Internet of Things (IoT). Miniaturized and lower-cost sensors lead to a growth in what, when, where, and how much data is collected and, more prominently, the capacity to attune the sensor to the specific data collection needed.
The fast miniaturization of technologies has made it possible to explore new modalities for sensor distribution, such as small satellites (smallsats) and unmanned aircraft systems (UAS, or drones) that can be quickly designed and deployed with orbits or flight paths customized to the mission. These mobile geospatial sensor platforms critically expand the capabilities of individuals, businesses, and government authorities to collect large volumes of remotely sensed data for varied and mission-critical purposes, including disaster response, environmental monitoring, and public safety.
Faster and wider wireless and web networks have started to address, in part, the growing demand for better methods of data transmission and geospatial data distribution to end-users. This is forming the groundwork for governments and consumers around the world to share and use spatiotemporal data, including for real-time apps.
Best GIS Software
Conform GIS is an advanced data visualization software provided as one of the chief products from GameSim which is known for producing super efficient, functional and top-notch data visualization products and services along with gaming support with such big companies in the industry such as Unity. Conform GIS is exclusively made for procedural planning and development enforcing simulation and modelling.
This GIS is an advanced program particularly focused for business purposes that unites Google Earth and its exclusive features together for exploiting the best of its tools for businesses. This advanced GIS measurement tool helps the professionals/businesses in gaining intricate details of any corner in the world, and the high-resolution printing and movie-making features help in generating comprehensive reports and presentations to generate business analytics and simultaneously come to the best decision to facilitate various sectors and industries for exponential business growth opportunities.
GRASS is a free open-source GIS solution that provides support to workgroups by using a map set or location and sharing data over the Network File System. GRASS GIS system comprises of 350+ modules that enables the users to manage location-based data and render maps and images. GRASS GIS has some powerful capabilities and supports various databases thus providing greater user satisfaction.
In order to make maps, this software has made its place However, this is not an atlas or a simple map viewing program. The basic changes that are done to the google map maker are said to appear on the google maps but only after the appropriate review. However, the reviews are also done by google moderators. Hence, the uniqueness of this software has never gone out of trend.
MyGov is a simple and cheap web-based. It helps to work from any place. Also, it allows working with the Community’s Development software suite. This is customizable and is easy to use. This can also be efficient to the office and custom workflow is another thing that needs to be mentioned. It will ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of any organization.
OnePlace is a powerful online map maker accessible on-the-go from as big as desktops to mere smartphones with user-friendly tools which need no experience or expertise for harnessing it efficiently. OnePlace is GIS mapping simplified with cloud-based support for efficient data and workflow management for all kinds of business and stakeholders to be on one page and be maximumly profitable to work immensely great even offline.
The fifteen years old OpenStreetMap GIS currently has more than 60 million active users and about 2 million registered users worldwide, making it one of the most used online maps worldwide. The intention of OpenStreetMap GIS was to promote the free use of data. There are several big tech giants using OpenStreetMap GIS for geolocation like – Apple Inc., Facebook, Flickr, MapQuest, Mapbox, Craigslist, Tesla, Moovit, Wikipedia, etc.
What3words GIS are available more than 35 languages and it integrates 3-word addresses which are unique, easy to say and share, and are accurate like GPS coordinates with bidirectional translation between what3words GIS address and latitude/longitude coordinates and has a website, apps for iOS and Android, and an API.



