Best Electric Vehicles
An electric car is an automobile propelled by one or more electric motors. An electric vehicle uses energy stored in rechargeable batteries, which can be charged using private or public charging infrastructure. There are 4 main types of electric vehicles, namely, battery electric vehicle (BEV), plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV), hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), and fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV).Battery Electric Vehicles, also known as BEVs, are fully-electric vehicles with rechargeable batteries and no internal combustion engine. Battery electric vehicles store electricity onboard with high-capacity battery packs. Their battery power is used to run electric motor and all onboard electronics. BEVs are ecofriendly vehicles as they do not emit harmful emissions and hazards caused by traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. BEVs are charged by electricity from an external source. Electric Vehicle (EV) chargers are classified according to the speed with which they recharge an EV battery.
PHEVs are powered primarily by electricity and can operate in an ‘all-electric’ mode like BEVs. In addition, they have a small conventional ICE that is used to enhance performance or extend the available range of the vehicle between charges. These vehicles emit CO₂ and other pollutants when ICE is in operation, but generally, at a lower level, with CO₂ emissions typically less than 50g/km.
HEVs use both electric motor and ICE and cannot be recharged by plugging into an off-vehicle power source. Instead, HEVs use regenerative brakes to recharge batteries. HEVs use electric motor and subsequently, gasoline engine comes into operation when load or speed increases. The two motors are controlled by an internal computer that ensures the best economy for driving conditions.
FCEV is a type of electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell instead of a battery or a combination with a battery or super capacitor to power its on-board electric motor.
Competitive Scenario
The electric vehicle market comprises several global market players that make it highly competitive. These players have adopted various strategies to expand their presence globally and increase their respective market shares. This section includes a study of the growth strategies adopted by market players from 2016 to 2019. The major strategies include new product developments, joint ventures, expansions, and acquisitions. The preferred strategies adopted by major players in the global electric vehicle market were new product developments, collaborations, partnerships, and mergers & acquisitions which accounted for a substantial share of all strategies adopted by companies during the period.
Competitive Leadership Mapping provides information about the major players that offer electric vehicles in the automotive industry and outlines the findings and analysis on how well each market vendor performs within the predefined micro-quadrant criteria. The vendor evaluations are based on two broad categories, namely, product offering and business strategy. Each category carries various criteria based on which the vendors are evaluated. The evaluation criteria considered under product offering includes the breadth and depth of offering, product features, and functionality, focus on product innovations, and product branding. The evaluation criteria considered under business strategy includes the overall revenue and growth rate (past 3 years), regional presence (based on geographic presence and presence in emerging markets), effectiveness of growth strategies—organic and inorganic (new product developments, expansions, mergers & acquisition, joint ventures, and partnerships & collaborations), vision alignment, and channel strategy and fit.
Tesla, BYD, BMW, Volkswagen, and Nissan lead the electric vehicle market and are recognized as visionary leaders. They have a strong portfolio of electric vehicle and services offerings. These players have been marking their presence in the electric vehicle market by offering various electric vehicles coupled with their robust business strategy to achieve constant growth in the electric vehicle market.
Renault, Hyundai, and Honda are recognized as dynamic companies in the electric vehicle market. They have a strong portfolio of electric vehicles and offer dynamic products across a multitude of vertical markets. Over the years, these vendors have been consistently growing in the electric vehicle market, and their market position is boosted by organic and inorganic ventures undertaken by them over the period.
Ford, Toyota, Ford, General Motors, and Daimler are recognized as innovators in the electric vehicle market. They have an innovative portfolio in the electric vehicle market and a robust potential to build strong business strategies for their business growth to be at par with the visionary leaders.
BAIC, Byton, JAC, KIA Motor, Rivian, and SF Motors are recognized as emerging players in the electric vehicle market. Most of the emerging vendors are boosting their sales capabilities across various regions by making global presence. The emerging companies are those who may hold a stronger position in the market in the future or considered as vanguards in other product segments but are at the initial growth stage in the electric vehicle market.
What are the major growth drivers in the Electric Vehicle Market?
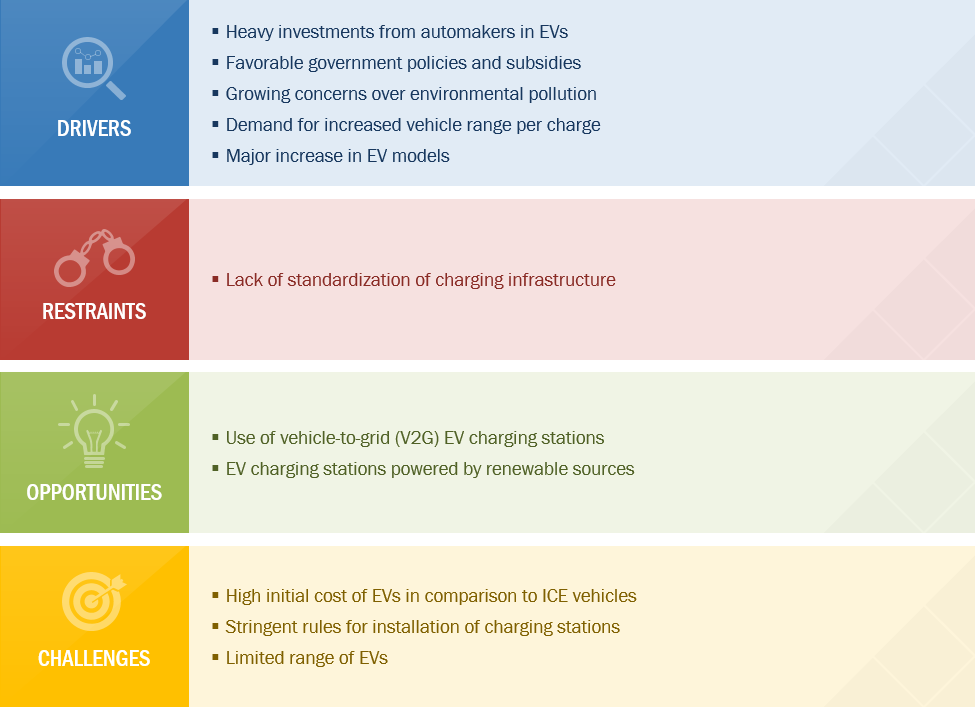
Favorable Government Policies and Subsidies
The governments of various countries have formulated stringent CO2 emission norms that have increased the demand for electric vehicles. Also, the governments are providing incentives and subsidies to encourage EV sales. The Chinese government will provide revised incentives of up to USD 3,700 for BEVs. These incentives from governments have also encouraged automakers to develop an increasing number of electric vehicles.
Several governments are providing various kinds of incentives such as low or zero registration fee and exemption in import tax, purchase tax, and road tax. Apart from providing subsidies, governments are also making favorable policies for the development of charging infrastructure. The US government recently invested USD 5 billion for promoting electric infrastructure. The federal Internal Revenue Service (IRS) tax credit is USD 2,500 to USD 7,500 per new EV purchased for use in the US. The size of the tax credit depends on the size of the vehicle and its battery capacity. A similar trend can be observed in European countries. Countries such as Norway and Germany are investing heavily in promoting EV sales. Thus, owing to the high amount of incentives and subsidies in Europe, a high growth rate in electric vehicle sales can be observed.
Heavy Investments from Automakers in EVs
Heavy investments from automakers are expected to cater to the growing demand for EVs and play a major role in the evolution of the electric vehicle market. Tesla, Volkswagen, Mahindra & Mahindra, Ford, Nissan, BMW, and General Motors have huge R&D budgets for the development of EVs. These OEMs offer electric vehicles in different segments ranging from small hatchbacks such as Nissan Leaf to high-end sedans like Tesla Model 3. The wide product offering has attracted many consumers and resulted in a growing market for electric vehicles. For instance, in January 2018, Ford announced an increase in planned investments in electric vehicles to USD 11 billion by 2022. The company plans to lineup 40 EVs by 2022, out of which 16 would be fully electric and 24 would be PHEVs. The investment figure is higher than a previously announced target of USD 4.5 billion by 2020. Ford’s expenses for engineering, research, and development in 2018 were USD 8.2 billion, up from USD 6.7 billion in 2015.
Growing Concern over Environmental Pollution
ICE vehicles emit a high volume of GHG into the atmosphere. To curb this, the governments of several countries have taken initiatives for the deployment of EVs. These initiatives would help in improving air quality. The use of EVs will reduce the dependence on fossil fuels. Further, electric vehicles require lesser maintenance and operating costs than ICE vehicles. EVs emit a lesser volume of GHG than ICE vehicles. According to estimations, GHG emissions from EVs are 50% less than conventional ICE vehicles. The use of renewable energies such as solar and wind for charging EVs would further help in minimizing carbon emissions. Thus, widespread adoption of EVs could significantly reduce carbon emissions globally.
Major Increase in EV Models
Expanding e-mobility is an important building block on the road to a CO2-neutral balance. Government regulations to promote the use of EVs are the driving factor in the increase of EV models by various companies. The number of EV models introduced by automotive companies is increasing rapidly with time. For instance, Volkswagen has announced to launch 70 new electric vehicles by 2028. In the North American region, Tesla has a strong product portfolio with 5 electric models already. Thus, increase in number of EV models will impact growth of the electric vehicle market significantly.
What are the major components used in Electric Vehicles?
Electric powered vehicles are gaining a rapid market share due to the increasing fuel problems. Electric cars are known to be very efficient as they consume less energy, making them environmentally friendly automobiles. The electric vehicle sales have increased demand for various components of electric vehicles such as batteries, instrument cluster, infotainment system, and on-board chargers. Batteries are the most important part of any electric vehicle as they provide power to the vehicle’s engine. Battery Management System (BMS) is also known as the brain of a vehicle as it manages the output, charging, and discharging of the battery. Therefore, determining how much electricity should flow through the battery with what speed. Every electric vehicle comes with an inbuilt rechargeable battery. Battery accounts for 70% of the weight of an electric vehicle. In the future, it is estimated to reduce significantly with the increase in the power holding capacity of a battery.
Infotainment systems may play an important role in the sales of vehicles. Latest technology upgradations such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are important technologies required by consumers. Infotainment systems play a vital role to add luxury and comfort in electric vehicles, experts believe all vehicles on the road are eventually going to be connected to each other, where these systems will play a significant role.
Batterry Cells and Packs
The composition of an EV battery might vary slightly depending on the types of electric vehicles, but generally, EV batteries are composed of cells, modules, and a pack. Most electric vehicle batteries are lithium based and rely on a mix of cobalt, manganese, nickel, and graphite and other primary components. The price of lithium-ion batteries has fallen steeply as their production scale has increased and manufacturers have developed more cost-effective methods. Expert forecast EVs to cost the same or less than a comparable ICE vehicle when the price of battery packs falls between USD 120 and USD 150 per kWh. Batteries in electric vehicles power the propulsion of electric vehicles. Electric vehicle batteries are rechargeable and are different from the SLI (Starting, Lightning, and Ignition) batteries. SLI batteries are used for starting, lighting, and igniting a vehicle. Batteries in electric vehicles are designed to provide power to the vehicle. The efficiency of an electric vehicle battery is measured by its high power-to-weight ratio, energy to weight ratio, and energy density. Batteries with less weight and size are responsible for the better performance of a vehicle. EVs also undergo various tests to secure batteries during a crash, chemical spillage from batteries, and isolating the chassis from the high-voltage system to prevent electric shock.
On-board Charger
The on-board charger receives AC input from the charging station and converts it to DC to charge a 350V or 650V battery. The use of common modules can reduce development costs by up to 5 %. Generally, these chargers are manufactured to be compatible with all international power grids and are designed to charge a vehicle battery pack quickly. On-board chargers are important for AC charging. DC fast chargers directly provide current to traction batteries and hence, do not require on-board chargers. On-board chargers are available in different range options (20, 30, and 40 amp) for different charging requirements. Recharging time for electric vehicles with level 1 and level 2 charging depends on the capacity of the on-board charger. Magna, Infineon, and Delphi are the leading manufacturers of on-board chargers for electric vehicles.
Fuel Stack
The fuel cell stack is the essential component of the fuel cell system. The fuel cell stack has two flow field plates and Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA). As the fuel cell stack generates electricity in the form of Direct Current (DC), a DC/AC converter should be used to convert the electricity to AC for AC applications in FCEVs. A fuel cell used for automotive applications generates less than 1.16 volts of electricity. Individual fuel cells are stacked to generate more power and electricity. This assembly is called a fuel cell stack. Fuel stack is the most expensive component of a fuel cell system. The size of stack defines the power output of the fuel cell. The number of fuel cell stacks can be increased to generate more power and electricity. The cost of per unit power generated by the fuel cell is inversely proportional to number of fuel cells in the stack. As the stack size increases, the cost of per unit power decreases. Hence, the fuel cell is efficient for long-range transportation. Also, with increasing research and development and investments by fuel cell manufacturers, OEMs, and governments, the cost of a fuel stack is expected to reduce. The cost of technological & operational improvements and regulatory requirements in the fuel cell technology in Europe is high. Moreover, due to economy of scale, per unit cost of the product decreases as the production volume increases.
What are the types of Electric Vehicles available in the market?
Passenger Car
A passenger car, as defined by the OICA, is a motor vehicle equipped with at least 4 wheels, comprising of not more than eight seats. The PC segment is the largest, by vehicle type, and includes sedans, hatchbacks, station wagons, Sports Utility Vehicles (SUVs), Multi-Utility Vehicles (MUVs), and other car types. This vehicle segment is the most promising market for electric vehicles, as it is the largest segment in the automotive industry. The passenger car segment of the electric vehicle market is growing at a significant rate in emerging economies in the Asia Pacific region. The market growth in the region can be attributed to a rise in the GDP and population, improvement in lifestyle, increased purchasing power of consumers, and development of infrastructure.
Electric passenger car is the fastest growing segment in the EV market and is expected to witness significant growth during the forecast period. The availability of a wide range of models, upgraded technology, increasing customer awareness, and availability of subsidies and tax rebates are the major factors driving the market.
Passenger cars account for the largest share in the electric vehicle market. The demand for passenger cars has increased due to the increase in demand for electric vehicles. Countries such as China have a low waiting period for electric vehicles compared to that for ICE powered vehicles. Due to the growing stringency of emission norms, European countries such as Germany are planning to have 1 million electric vehicles on the road by 2020. China dominates the market for passenger electric cars, followed by the US.
Commercial Vehicles
The commercial vehicle segment includes LCVs and HCVs. HCVs combine 2 categories of vehicles − heavy trucks and buses & coaches. The nature of these vehicles limits their production volume and growth rates as they are used in specific applications such as logistics, construction, and mining industries. On the other hand, LCVs have come a long way from having bare-essential features to full-blown utility vehicles that can be used for passengers as well as commercial purposes.
China is the biggest market for electric commercial vehicles owing to support from the government and contribution from the major manufacturers. In December 2018, the electric vehicle manufacturer Tesla started installing its production equipment in Shanghai, China.
The Chinese government, for tracking the growth of commercial electric vehicles, has also added a new aspect in the existing regulation in the form of a reporting system. The reporting system requires public transport companies and local authorities to regularly submit the status of electric buses in the local public transport sector. This system is expected to help the government in monitoring the progress of electric bus deployment and identifying additional policy measures that may be required to promote the sales of electric buses in the country further.
What are the various Charging Points available which can be used to charge Electric Vehicles?
Increased electric vehicle sales have increased the demand for charging infrastructure to recharge the electric vehicles. Several types of electric chargers are available, with charging stations differing mainly based on the speed of charging. There are two major types of charging types―Normal Charging and Super charging. Normal Charging need more time to charge vehicles compared with the Super charging. As they are DC chargers, Super charging offer high-speed charging; whereas, normal charging are AC charging points. Vehicles with AC charging require an on-board charger to convert AC into DC. Conversion of AC to DC is important because electric vehicles have DC batteries. DC is easy to store, but AC cannot be stored in batteries.
About 95% of the vehicle charging is done using normal charging installed in homes. Apart from DC fast chargers, all home charging units use EVSE. The EVSE is also known as a home charger or wall charger. EVSE is the unit that converts AC into DC using the car’s onboard charger.
Superfast chargers add more miles per hour of charging than normal charging do. Super charging consume more electric energy than normal charging do. The charging capacity differs from vehicle to vehicle. Some vehicles in the market do not have the super charging option.
Normal Charging
Normal charging market in Asia pacific is estimated to the largest market in terms of charging points. The region comprises some of the fastest-developing economies of the world such as China and India. The Government of India, in order to increase the adoption of electric vehicles, has announced plans for financial support—a zero-rated goods and services tax (GST) for a window of 3 years for EVs. This would lead to an increase in electric vehicle production volumes over the years, which would cater to both the domestic and the overseas demand. Japan and China export electric vehicles across the globe.
Super Charging
Super charging are high DC charging units. DC charging station delivers a maximum power of 240 kW, supplying a high current of up to 400 A at a voltage of up to 600 VDC. Super charging is a highly-powered charging option, with the potential to fully recharge an EV in less than 30 min. However, it is very expensive. DC charging stations cost around USD 15,000–40,000. In a DC fast charging system, the AC/DC conversion occurs in the charging equipment rather than in a vehicle's AC/DC converter, so that the power entering the vehicle is already in DC.
Most residential electrical services do not provide the capacity of electrical power that super charging station delivers, thus making super charging infeasible for implementation at homes. Companies involved in the development of DC charging Stations include ABB, Schneider Electric, EVTEC, ChargePoint, Bosch Automotive Service Solutions, Signet Systems, and Tesla Motors.
What are the major trends affecting the Electric Vehicle Market?
Shared Mobility
Shared mobility allows drivers to borrow EVs on a short-term basis. Considering the cost of EVs, shared mobility is a cost saving option and is being adopted across the globe. Most car sharing services implement their operation in two ways—free-floating systems where cars can be parked anywhere or hub services where cars must be left in designated parking spots. In recent years, smartphones and mobile connectivity have made free-floating systems easier to access and pay. Although free floating systems have operational challenges as they have to rely on limited number of public charging stations. This drawback can be overcome in hub services as drivers can charge the EVs at slower speed and cheaper price with their own chargers. Many service providers such as Uber, Ola, Lyft, Didi Chuxing, and GrabTaxi are implementing such shared mobility services.
Batteries Used in Solar Vehicles
There are 3 types of batteries, namely, lead-acid, lead carbon, and lithium-ion, which are widely used in solar vehicles. The solid-state battery (SSB) is the future of solar vehicle batteries—it is an emerging technology and not yet commercialized. Solid-state battery manufacturers are planning to commercialize the technology by 2020. The batteries used for solar vehicles differ in many characteristics such as energy storage efficiency, speed, recharging time, reliability, cost, safety, and consistent performance.
Smart Charging System
A smart charging system helps optimize the charging process by generating and efficiently distributing available power. The implementation of a smart charging system helps reduce unnecessary cost as the available power for charging is utilized efficiently. Smart charging enables load balancing and distributes the available power capacity proportionally over all active charging stations. It also helps gather vital charging data generated from multiple stations with a single cloud-based management platform. Such type of charging also prevents excessive costs by reducing or pausing a charging session if the power consumption is above the specified level, which is called peak shaving.
Best Electric Vehicle
BMW is a leading manufacturer of luxury cars. The company build powerful electric cars by extensively using its own eDrive technology. The group comprises brands such as BMW (Germany), MINI (UK), and Rolls-Royce (UK). BMW is also highly focused on future markets, with company’s unique strategy plan “Strategy Number One”. In this plan, the company will focus on hybrid and electric vehicles as the future technology powering its vehicles.
Continental has its presence in 554 locations and operates in 61 countries globally. Continental invested USD 3.7 billion in R&D in 2018, which highlights the company’s focus on its R&D activities.
Daimler’s strength lies in the reach that the company has. The company has manufacturing facilities in 19 countries and more also has than 8,500 sales centers across North America, Europe, Asia Oceania, and RoW. The company has also been focused on intelligent electromobility.
Ford develops Electric Vehicles that have a higher instant torque, zero tail pipe emissions and require no oil changes. Ford also offers an excellent network of charging points ranging from a full-fledged charging station to wall mounted mobile charging stations.
Honda developed a new hybrid model as part of the Honda Electrification Initiative, which will expand the company's portfolio of electrified vehicles. Honda is also working on using its innovative two-motor hybrid powertrain from passenger cars to its light truck lineup in the future.
Hyundai has developed an electric car that has the capacity to cover approximately 452 kms in a single charge and is apure EV that emits no carbon. Hyundai also has been developing a new smartphone-electric vehicle pairing-based performance adjustment technology, which allows users to customize primary functions through a smartphone application—an industry-first innovation.
Nissan Motors is a leading manufacturer of vehicles under the Nissan, Infiniti, and Datsun brands worldwide. The company offers vehicle and vehicle parts, engines, manual transmission, specially equipped vehicles, industrial equipment engines, and so on. The company also manufactures electric vehicles. It offers BEVs to customers. It focuses significantly on R&D, and made huge investments in research-related operations in 2018.
Tesla designs, develops, manufactures, and sells high-performance fully electric vehicles and energy generation and storage systems. Tesla Roadster was the first EV launched, in 2008, followed by the Model S and many others. The company has presence in almost every part of the world, but the major part of revenue comes from the US. The company inaugurated its Giga factory at Nevada, US, in the year 2016 to accelerate growth by producing batteries as per requirement. In 2019, it launched the first fully electric compact SUV named Model Y. Tesla Motors has plans to launch four EVs including BEVs and PHEVs by 2021.
Volkswagen is a well-established automotive manufacturer who produces cars under 12 different brands - Volkswagen Passenger Cars, Audi, SEAT, ŠKODA, Bentley, Bugatti, Lamborghini, Porsche, Ducati, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles, Scania and MAN. The company has a diversified product portfolio that gives it a sustainable position in the current market and reduces reliance on a single product. It also gives a solid base for further expansion in the electric vehicle market.
Volvo’s main USP is the safety that it builds in every car that it manufactures. Also, the company has been focused on manufacturing environment friendly electric vehicles that have zero emissions and larger batteries that would enable owners to cover maximum distance.

- Enterprise
- SME
- Startups
 In this current age is considered age of electromobility, growing emissions caused due to vehicles, and strict regulations imposed by governments have compelled automakers to produce modes of transport which are environmentally sound and also inexpensive for the general public. This has increased the adoption of electric vehicles. Electric vehicles produce minimal air pollutants. Also, battery electric vehicles produce lower noise due to the absence of an IC engine.
In this current age is considered age of electromobility, growing emissions caused due to vehicles, and strict regulations imposed by governments have compelled automakers to produce modes of transport which are environmentally sound and also inexpensive for the general public. This has increased the adoption of electric vehicles. Electric vehicles produce minimal air pollutants. Also, battery electric vehicles produce lower noise due to the absence of an IC engine.
The electric vehicle market is estimated to reach 21,839 thousand units by 2030. Proactive OEM response, decreasing price of batteries, funding, subsidies and incentives, growing demand for electric vehicles, increasing concern of environmental pollution, and huge investments by electric vehicle leaders are driving the growth of the electric vehicle market.
Heavy investments from Top Electric Vehicle Companies to drive this market
This report identifies and benchmarks the top Electric Vehicle companies such as Tesla (US), BYD (China), BMW (Germany), Volkswagen (Germany), and Nissan (Japan), and evaluates them on the basis of business strategy excellence and strength of product portfolio within the electric vehicle ecosystem, combining inputs from various industry experts, buyers, and vendors, and extensive secondary research including annual reports, company press releases, investor presentations, free and paid company databases. They are rated and positioned on a 2x2 matrix, called as ‘Company Evaluation Quadrant’, and identified as Visionary Leaders ( best electric vehicle manufacturers ), Dynamic Differentiators, Innovators, or Emerging companies.
The report includes market-specific company profiles of 25 electric vehicle manufacturers and assesses the recent developments that shape the competitive landscape of this highly fragmented market. The report identifies the best electric vehicle manufacturers after a thorough evaluation.
Electric vehicle quadrant report identifies and benchmarks the best electric vehicle manufacturers such as Tesla (US), BYD (China), BMW (Germany), Volkswagen (Germany), and Nissan (Japan), and evaluates them on the basis of business strategy excellence and strength of product portfolio within the electric vehicle ecosystem, combining inputs from various industry experts, buyers, and vendors, and extensive secondary research including annual reports, company press releases, investor presentations, free and paid company databases. They are rated and positioned on 2x2 matrix, called as ‘Company Evaluation Quadrant’, and identified as Visionary Leaders ( best electric vehicle manufacturers ), Dynamic Differentiators, Innovators, or Emerging companies.
SAMPLES:




- Updated version of this Quadrant
- Different Company Evaluation Quadrant
- 'Startup Only' Company Evaluation Quadrant
- Region or Country specific evaluation
- Application or Industry specific evaluation ..Read More
- Submit a Briefing Request
- Question about our published research
- Request for evaluation of your organization for specific market
- Request for re-evaluation of Company Evaluation Quadrant ..Read More



