Comparing 12 vendors in Location-based Entertainment Startups across 0 criteria.
Become a Client
- Access Exclusive Reports, expert insights and tailored support to drive growth.
The location-based entertainment (LBE) market is evolving significantly, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. Characterized by immersive and interactive experiences, LBEs are becoming popular as they seamlessly integrate digital elements with physical environments. Currently growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.4%, the market presents considerable opportunities for businesses aiming to enhance user engagement through unique offerings. This growing popularity is fueled by the incorporation of cutting-edge technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and artificial intelligence (AI), which allow for innovative experiences that captivate audiences.
Key market components include the desire for shared social experiences and the consumer shift towards service and experience-based spending over material goods.
Furthermore, there is a burgeoning demand for customized, immersive experiences that blur the lines between the virtual and real worlds. This shift is supported by a rising disposable income and a growing preference for experiences that provide emotional engagement and participation.
Markets are seeing new entries due to reduced technological barriers, facilitating greater competition and innovation. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs, weather dependency, and regulatory hurdles remain prevalent. The market witnesses intense competitive rivalry from established entities and dynamic startups, pushing the envelope in terms of price and experience innovation.
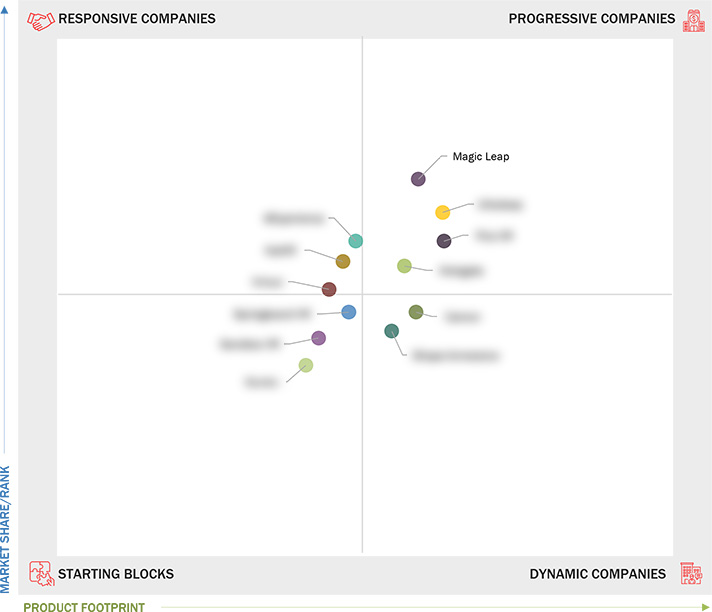
Startups in the Market
Springboard VR: Founded in 2016 in Agoura Hills, California, Springboard VR is a technology firm that specializes in creating virtual reality experiences for businesses. It provides innovative VR solutions tailored for arcades and entertainment venues.
4Experience: Based in Slaskie, Poland, 4Experience is recognized for its responsive VR solutions. It offers custom experiences to meet current market demands. Established in 2014, the company is supported by venture capital.
Hologate: Operating out of Bayern, Germany, Hologate is a leading provider of arcade VR systems. Since its inception in 2017, it has been known for its venture capital-backed growth. It offers exciting, immersive environments primarily for gaming.
Ultraleap: Founded in the UK, Ultraleap focuses on gesture recognition technologies and has made significant strides with its Series D funding. It serves a broad array of clients across multiple regions.
Magic Leap: This Florida-based company is notable for its breakthrough in spatial computing, offering advanced AR solutions. Since 2011, it has garnered substantial private equity, fueling its technological advancements.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.2.1 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3 Market Scope
1.3.1 Market Segmentation
1.3.2 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Stakeholders
1.6 Summary of Changes
2 MARKET OVERVIEW
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Rising consumer spending power
2.2.1.2 Advancements in VR and AR technologies
2.2.1.3 Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine
learning (ML) technologies
2.2.1.4 Rising demand for social and shared experiences
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 Limited scalability of Location-based entertainment
business
2.2.2.2 High upfront cost
2.2.2.3 Impact of wealth dependency
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Increase in live events and performances
2.2.3.2 Rising popularity of wearables such as fitness trackers and
smartwatches
2.2.3.3 Collaboration with brands & events
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Regulatory requirements at local, state, and federal levels
2.2.4.2 Rapid pace of technological change
2.2.4.3 Limited appeal
2.3 Brief History of Location-based Entertainment
2.4 Ecosystem Analysis
2.5 Case Study Analysis
2.5.1 Andretti Karting Enhances Location-based Entertainment Operations
with Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central
2.5.2 Worldbuildr Utilizes Unity Industry for AEC to Power Next-
Generation Virtual World Creation
2.5.3 Maquette Utilizes Optitrack Motion Capture By Naturalpoint for
Enhanced XR Prototyping
2.5.4 Dreamtrace Utilizes 4experience for Motion Tracking and
Multiplayer Functionalities in Physical VR Arena
2.5.5 Fennec Labs and Spawnpoint Utilize Vive Focus 3 and LBSS to Deliver Engaging VR Arcade Experiences
2.5.6 Atlantis Aquarium Relies on Panasonic to Offer Fully Immersive
Experience of Underwater World
2.6 Supply Chain Analysis
2.7 Regulatory Landscape
2.7.1 Regulatory Bodies, Government Agencies, and Other Organizations
2.7.1.1 International Association of Amusement Parks and
Attractions (IAAPA) – Global
2.7.1.2 Federal Communications Commission (FCC)-Global
2.7.1.3 Gambling Regulatory Authority of Singapore (GRA)-Global
2.7.2 Key Regulations
2.7.2.1.1 North America
2.7.2.1.2 Europe
2.7.2.1.3 Asia Pacific
2.7.2.1.4 Middle East & Africa
2.7.2.1.5 Latin America
2.8 Pricing Analysis
2.8.1 Pricing of Solutions, By Key Player,2024
2.8.2 Indicative Pricing Analysis, By AR Software,2024
2.9 Technology Analysis
2.9.1 Key Technologies
2.9.1.1 Virtual Reality (VR)
2.9.1.2 Augmented Reality (AR)
2.9.1.3 Projection Mapping
2.9.2 Complementary Technologies
2.9.2.1 Artificial intelligence (AI)/ Machine learning (ML)
2.9.2.2 Internet of Things (IoT)
2.9.2.3 5G
2.9.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.9.3.1 Wearable devices
2.9.3.2 Cloud computing
2.10 Patent Analysis
2.11 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.11.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.11.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.11.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.11.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.11.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
2.12 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.13 Key Stakeholders and Buying Criteria
2.13.1 Key Stakeholders in Buying Process
2.13.2 Buying Criteria
2.14 Key Conferences and Events, 2025–2026
2.15 Technology Roadmap for Location-based Entertainment Market
2.15.1 Short-Term Roadmap (2023–2025)
2.15.2 Mid-Term Roadmap (2026–2028)
2.15.3 Long-Term Roadmap (2029–2030)
2.16 Best Practices in Location-based Entertainment Market
2.16.1 Seamless Integration of Technology
2.16.2 Personalization of Experiences
2.16.3 Focus on Hygiene and Safety
2.16.4 Scalability of Infrastructure
2.17 Current and Emerging Business Models
2.17.1 Pay-Per-Experience Model
2.17.2 Subscription Model
2.17.3 Partnership & Licensing Model
2.17.4 Freemium Model
2.17.5 Data Monetization
2.18 Location-based Entertainment Market: Tools, Frameworks, and Techniques
2.19 Trade Analysis
2.19.1 Export Scenario of Video Game Consoles, Machines, and Other
Articles for Funfair, Table, or Parlor Games (9504)
2.19.2 Import Scenario of Video Game Consoles, Machines, and Other
Articles for Funfair, Table, or Parlor Games, By Key Country,
2016–2023 (USD Billion)
2.20 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.21 Impact of Generative AI on Location-based Entertainment Market
2.21.1 Top Use Cases and Market Potential
2.21.1.1 Key Use cases
2.21.2 Best Practices
2.21.2.1 Hospitality & tourism
2.21.2.2 Retail & shopping malls
2.21.2.3 Sports & live entertainment
2.21.3 Case Studies of Generative AI Implementation
2.21.3.1 AI-powered virtual tour guide enhancing visitor engagement
2.21.3.2 Smart AI concierge improving guest satisfaction in theme
parks
2.21.3.3 AI-generated gamified retail experience boosting foot
traffic in shopping malls
2.21.4 Client Readiness and Impact Assessment
2.21.4.1 Client A: Powered personalized storytelling
2.21.4.2 Client B: Intelligent virtual assistants & concierges
2.21.4.3 Client C: AI-driven gamifica
3 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win,
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.5 Market Ranking Analysis
3.6 Company Evaluation Matrix: Key Players
3.6.1 Stars
3.6.2 Emerging Leaders
3.6.3 Pervasive Players
3.6.4 Participants
3.6.5 Company Footprint: Key Players
3.6.5.1 Regional footprint
3.6.5.2 Offering footprint
3.6.5.3 Venue footprint
3.6.5.4 Application footprint
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SME
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs
3.8 Competitive Scenario and Trends
3.8.1 Product Launches
3.8.2 Deals
3.9 Brand/Product Comparison Analysis
3.10 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics of Key Location-based
Entertainment Market Providers
4 COMPANY PROFILES
4.1 SPRINGBOARDVR
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 4EXPERIENCE
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 HOLOGATE
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 ULTRALEAP
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 MAGIC LEAP
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
4.6 SHAPE IMMERSIVE
4.6.1 Business overview
4.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.6.3 Recent developments
4.7 CAMON
4.7.1 Business overview
4.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.7.3 Recent developments
4.8 KATVR
4.8.1 Business overview
4.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.8.3 Recent developments
4.9 VIRTUIX
4.9.1 Business overview
4.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.9.3 Recent developments
4.10 PICO
4.10.1 Business overview
4.10.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.10.3 Recent developments
4.11 ILLUMIX
4.11.1 Business overview
4.11.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.11.3 Recent developments
4.12 SANDBOX VR
4.12.1 Business overview
4.12.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.12.3 Recent developments
Latest
HOLOGATE celebrates year of expansion as VR system goes wireless
 Dec 2024
Dec 2024 Blooloop
BlooloopRheinmetall, Hologate partner on XR, VR simulations
 Dec 2024
Dec 2024 Asia Pacific Defence Reporter
Asia Pacific Defence ReporterGoogle Contracts Employees From Magic Leap
 Dec 2024
Dec 2024 The Information
The InformationMagic Leap founder is back with $20M funding round for SynthBee
 Oct 2024
Oct 2024 VentureBeat
VentureBeatSaudi PIF Has Poured $750 Million Into Depleted AR Firm Magic Leap
 Aug 2024
Aug 2024 Bloomberg
BloombergInside Sandbox VR: Dublin’s new virtual reality experience that doubles as a workout
 Apr 2025
Apr 2025 Business Post
Business PostSandbox VR surpasses $200M in lifetime sales with 150 more locations in the pipeline
 Apr 2025
Apr 2025 VentureBeat
VentureBeatFor the First Time in Münster: Sandbox VR Opens at Ufer Studios
 Apr 2025
Apr 2025 Eagle-Tribune
Eagle-TribuneCompany List