Comparing 4 vendors in Cloud ERP startups across 0 criteria.
Become a Client
- Access Exclusive Reports, expert insights and tailored support to drive growth.
The Cloud ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) industry is at the cusp of a transformative era, shaped by the fusion of new technologies and evolving business needs. This comprehensive report offers a nuanced evaluation of the dynamic landscape of Cloud ERP solutions in 2024, spotlighting how these technological solutions are becoming indispensable for modern enterprises. The ERP market has shown remarkable growth, driven by the rapid adoption of cloud-based solutions, as companies strive for improved efficiency and scalability. The increasing integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into ERP systems signifies a paradigm shift towards data-driven decision-making frameworks that empower businesses with actionable insights. Furthermore, the rising demand for business process automation has propelled organizations to invest in robust ERP solutions that transcend traditional functionalities, providing operational efficiencies and enhanced customer experiences.
The advent of remote work and the burgeoning expectations from mobile workforces have further underscored the necessity for flexible and accessible ERP systems operating seamlessly across diverse geographical landscapes. In parallel, firms are confronting challenges such as integration with legacy systems, data security concerns, and the complexities associated with vendor selection—barriers that the next-generation ERP solutions must adequately address.
Emerging startups and established vendors leverage strategic partnerships, novel product offerings, and mergers and acquisitions to capture market share and bolster their offerings. This vibrant ecosystem is marked by continuous innovation, where startups play a pivotal role, driving agility and responsiveness with tailor-made solutions that cater to industry-specific demands.
The Cloud ERP market is rapidly evolving, marked by technological disruptions and strategic realignments. As businesses strive to navigate this landscape, this report's insights equip decision-makers with valuable knowledge about industry trends, key players, competitive benchmarking, and the strategic paths being carved out by startups, setting a definitive course for the future of enterprise resource planning.
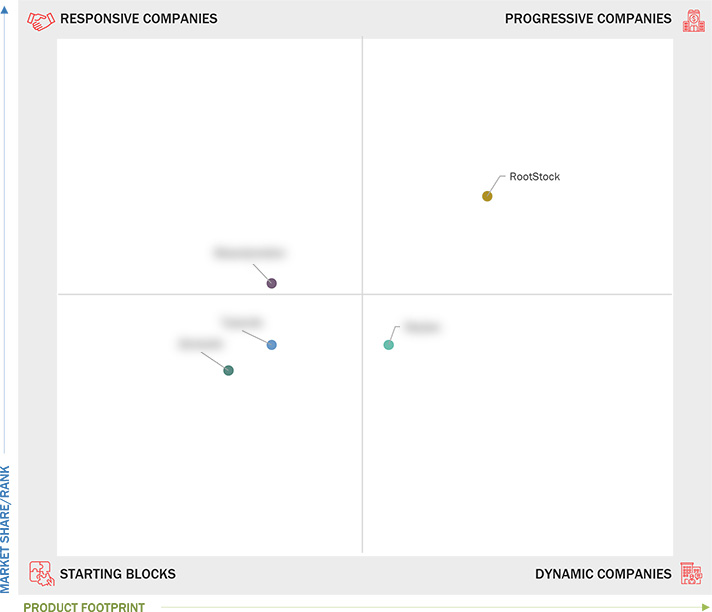
Startups in the Market
Zenscale: Based in Ludhiana, Punjab, India, Zenscale offers robust cloud ERP solutions tailored for various industries. The company's introduction of ZENAPS, an advanced planning solution, empowers manufacturers with improved efficiency by enabling real-time workflow adjustments.
RootStock: Headquartered in San Ramon, California, RootStock is recognized as a progressive player in the market with its strong portfolio of modular data center solutions. The company has established a solid market presence through innovative solutions and strategic growth initiatives.
BizAutomation: Operating from Santa Ana, California, BizAutomation is a responsive company that delivers a unified cloud ERP and supply chain management platform. The company is distinguished by its single-version SaaS model, which helps eliminate inefficiencies through real-time data integration.
Tyasuite: Bangalore-based Tyasuite is acknowledged as a starting block in the cloud ERP sector. It drives innovation through multiple product developments to enhance sales capabilities and provide integrated solutions across client bases.
Reybex: Situated in Essen, Germany, Reybex is classified as a dynamic company owing to its extensive channel partner network and a consistent track record of revenue growth driven by innovative ERP solutions tailored to various verticals.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.2.1 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3 Market Scope
1.3.1 Market Segmentation
1.3.2 Years Considered
1.4 Currency
1.5 Stakeholders
2 MARKET OVERVIEW AND INDUSTRY TRENDS
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Fusion of AI and ML within Cloud ERP for informed decision-
making
2.2.1.2 Rising spending on cloud-based services/software
2.2.1.3 Increasing focus on business process automation and
operational efficiency
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 High risk of data security
2.2.2.2 Restricted personalization hinders Cloud ERP growth
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Growth of mobile and remote workforce demands efficient
Cloud ERP solution
2.2.3.2 Growing demand from small and medium enterprises (SMEs)
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Integration challenges with existing legacy systems and
processes
2.2.4.2 Complexity of vendor selection and due diligence processes
2.3 Case Study Analysis
2.3.1 Lexington Enhanced Financial Efficiency in Healthcare with Oracle
Cloud ERP
2.3.2 Fieldfisher Leveraged Microsoft Dynamic 365 for Business Continuity
2.3.3 Tasi Measurement Standardized Operations with Epicor Kinetic
2.3.4 Boca Terry Improved Productivity and Customer Service with
Acumatica ERP
2.3.5 Mlw Foods Achieved 30% Cost Savings with Sage X3 Implementation
2.4 Supply Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Technology Analysis
2.6.1 Key Technologies
2.6.1.1 AI & ML
2.6.1.2 Multi-tenant & Microservices Architecture
2.6.1.3 Low-code/No-code Development
2.6.1.4 Big Data & Analytics
2.6.2 Complementary Technologies
2.6.2.1 Customer Relationship Management
2.6.2.2 Human Capital Management
2.6.2.3 Manufacturing Execution Systems
2.6.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.6.3.1 Cloud Infrastructure
2.6.3.2 Middleware & APIs
2.6.3.3 Cybersecurity & Identity Management
2.7 Pricing Analysis
2.7.1 Average Selling Price (ASP) of Key Players, By Organization Size
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.9 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.9.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.9.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.9.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.9.4 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.9.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
2.10 Regulatory Landscape
2.10.1 Regulatory Bodies, Government Agencies, and Other Organizations
2.10.2 Regulations, By Region
2.11 Trends and Disruptions Impacting Customers’ Businesses
2.12 Key Stakeholders and Buying Criteria
2.12.1 Key Stakeholders in Buying Process
2.12.2 Buying Criteria
2.13 Business Model Analysis
2.13.1 Subscription-Based Model
2.13.2 License-Based Model
2.13.3 Freemium Model
2.14 Key Conferences and Events (2024–2025)
2.15 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.16 Impact of AI/Gen AI on Cloud Service Brokerage
2.16.1 Top Clients Adapting Gen AI
2.16.1.1 Microsoft
2.16.1.2 Oracle
2.17 Case Studies
2.17.1 FC Bayern’s Sap-Powered AI ERP Transformation
3 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Strategies Adopted By Key Players/Right to Win
3.3 Market Share Analysis
3.4 Revenue Analysis, 2019–2023
3.5 Company Evaluation Matrix: Key Players,2023
3.5.1 Stars
3.5.2 Emerging Leaders
3.5.3 Pervasive Players
3.5.4 Participants
3.6 Brand/Product Comparison
3.6.1 Company Footprint
3.6.2 Company Footprint: Key Players,2023
3.6.2.1 Company footprint
3.6.2.2 Region footprint
3.6.2.3 Offering footprint
3.6.2.4 Application footprint
3.6.2.5 Deployment type footprint
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs,2023
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs,2023
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of startups/SMEs
3.8 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics of Key Vendors
3.8.1 Company Valuation
3.8.2 Financial Metrics
3.9 Competitive Scenario
3.9.1 Product Launches
3.9.2 Deals
4 COMPANY PROFILES
4.1 ROOTSTOCK SOFTWARE
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 ZENSCALE
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 BIZAUTOMATION
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 TYASUITE
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 REYBEX
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
Latest
Rootstock Software Unveils Winter ‘25 Release
 Dec 2024
Dec 2024 businesswire
businesswireRootstock Software Names Andy Brabender as Chief Revenue Officer
 Aug 2024
Aug 2024 businesswire
businesswireCompany List