Warehouse Management System
Updated as on -
Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software application that helps manage operations in warehouses in the most efficient and productive manner. Functions of these systems include inventory control, labour management, yard management, and dock management, among others. A WMS can be deployed on premise or can be accessed through cloud servers maintained by WMS vendors. Based on their feature and functionality, WMS software packages are available in 3 tier types—advanced (tier 1), intermediate (tier 2), and basic (tier 3). The warehouse management system market is estimated to be at $2.4 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $ 5.1 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 16.0%.
Best Warehouse Management System for 2020
A Warehouse Management System helps in improving inventory management by reducing inventory levels, enhancing order completion, and decreasing order cycle time. These systems have been created to manage all of the warehouse activities. They enable businesses to monitor each asset down to the lowest level of detail for an enhanced order fulfilment and inventory precision. It make inventory management a much quicker, simpler and effective task. Best Warehouse Management Systems provide quick, accurate and real time response so that organizations can respond faster to the demands of their customers. The above mentioned is just a glimpse into what Warehouse Management Systems are capable of doing. As we go further, we will learn in detail about the Warehouse Management Systems providers, the importance of warehouse management systems, and the latest trends and developments. Listed below are the best Warehouse Management system:
Top Warehouse Management System
- Epicor
- Manhattan Associates
- Zoho Inventory
- SAP
- HighJump
- Infor
- JDA
- PTC
- 3PL Warehouse Manager
- BLUJAY SOLUTIONS
Epicor - Epicor is a specialist is providing Fully Integrated Warehouse Management solution and Supply Chain Systems. The company’s best warehouse management system helps businesses with having total control, management, and getting better visibility of their logistics and Supply Chain Management operations. The company’s warehouse management system delivers all the functionality required to manage all facets of your order fulfilment, warehousing, and distribution requirements….Read more
Manhattan Associates - Manhattan offers warehouse management software solution that is highly mobile and flexible. This warehouse management software solution leverages progressive Artificial Intelligence, machine learning technology and exclusive algorithms for the purpose of orchestration of the industry’s first Warehouse Execution System (WES) inside a Warehouse Management System. Manhattan’s warehouse management systems also help in enhancing order fulfilment and quantity for both WAVE and WAVELESS order fulfilment concurrently in a single platform….Read more
Zoho Inventory - Zoho offers warehouse management software solution, with which businesses can manage several warehouses, move stock between them and create reports that help in getting better insights and visibility into warehouse management operations. The company’s warehouse management systems allow users to control different warehouses located at separate location only with a single application….Read more
SAP - SAP offers Warehouse Management Solution that provide flexible and automated support in processing all goods transfers and in handling stocks in the warehouse facility. The system also supports planned and well-organized processing of all the logistics processes in the warehouse. The company’s WMS allows businesses to map their whole warehouse complex in detail down to the storage bin level….Read more
HighJump - HighJump offers cloud-based warehouse management solution which provide the tools required to connect and enhance the warehouse management and supply chain operations. HighJump WMS in the cloud, is an end-to-end warehouse management suite that offers inventory management, labour performance enhancement, warehouse processes, and material flow management. The company’s Warehouse Management Systems powers several retailers, wholesalers, manufacturers and also third-party logistics providers….Read more
Infor - Infor offers CloudSuite WMS solution that is capable of providing excellent visibility into inventory, orders, equipment, and people to enable organizations to enhance their service levels and product velocity. CloudSuite WMS enables organizations to handle their distribution centre activities holistically. The solution also integrates warehouse fulfilment with embedded labour management and 3D visual analysis to decrease difficulty and support improved operational execution….Read more
JDA - JDA Warehouse Management solution provides an exhaustive, real time visibility into all warehouse activities, offers real-time insights on inventory, personnel and equipment performance across all channels. The platform has been created to be receptive to the demands of Omni channel workplace, offering visibility across various channels, geographies, suppliers, and locations….Read more
PTC - PTC MOVE WMS solution allows businesses to enhance warehouse activities within the distribution centre and extended network so that they can improve their revenues. The system can be configured easily and can also be ported with fast UAT/QA verification with no downtime. It also offers real-time updates and routine operational status from virtually any location….Read more
Market Overview
A warehouse management system is a software solution primarily used by warehouse operators for efficient control over various warehousing operations, including inventory management, labor management, cross-docking, picking and placing, packaging, shipping, yard management, and dock management. A WMS can be deployed on-premise or on-cloud in different industries, such as third-party logistics (3PL), e-commerce, automotive, electrical and electronics, food & beverages, and pharmaceuticals.
This section describes the mapping of top 25 players in the Warehouse Management System market. These players are ranked on the basis of 2 major factors - business strategy excellence and strength of product portfolio. The detailed rating is given on the basis of product offerings and business strategies of 25 companies that belong to the ecosystem of the Warehouse Management System market.
Business strategy excellence describes how players are increasing their presence in the market. The factors considered in the “business strategy excellence” section are rated on the basis of the performance of the company in the Warehouse Management System market. Factors such as geographic footprint, effectiveness of growth strategy, and technology innovation have been considered while rating the business strategy excellence section of the company.
The strength of product portfolio describes players’ approach toward launching warehouse management system based product offerings and innovations. The factors in “strength of product portfolio” section are rated on the on the basis of the WMS software, hardware and services offered by each player in the Warehouse Management System market. Factors such as focus on product innovation; breadth and depth of product offering, and product feature and functionality have been considered while rating the strength of product portfolio section of the company.
Visionary leaders in the Warehouse Management Software market generally receive high scores for most evaluation criteria. They have a strong service portfolio, a robust market presence, and effective business strategy. Visionary leaders are the leading market players in terms of new developments such as product launches, innovative technologies, and adoption of growth strategies. These players have a broad portfolio of products that cater to most regions worldwide. Visionary leaders primarily focus on acquiring the leading market position through their strong financial capabilities and well-established brand equity. The companies included in the Visionary Leaders quadrant are Manhattan Associates, Blue Yonder (JDA Software), HighJump (Körber), Oracle, and SAP.
Dynamic differentiators in the Warehouse Management System market are established vendors with very strong business strategies and a decent product portfolio. They generally focus on a specific type of technology related to the product. There are many companies in the Warehouse Management System market who largely depend on their competitive R&D. These players have established business channels and required resources, but offer less competitive products compared to visionary leaders. The companies in this quadrant are PSI, Mantis, MadE4Net, BluJay Solutions, and Synergy Logistics.
Innovators in the Warehouse Management Solution demonstrate substantial product innovations compared to their competitors. They have a highly focused product portfolio. However, they do not have very strong growth strategies for their overall business. New players can make steady profits even if there is a high demand for innovative warehouse management system products. These players hold a smaller share in the market but have innovative products portfolio and services in the Warehouse Management System market. The players are IBM, Infor, Tecsys, and PTC.
Emerging companies in the Warehouse Management System have niche service offerings and are starting to gain their positions in the market. They do not have very strong business strategies compared to other established vendors. They can be new or old entrants in the market and may require some more time before gaining significant traction in the market. The players in this category are Epicor Software, Dematic, Nulogy, Vinculum Solutions, Microlistics, Datapel, Cantaloupe Systems, 3PL Central, Reply, Genertix Group, and Softeon.
The below image represents the type of strategies adopted by players in the market: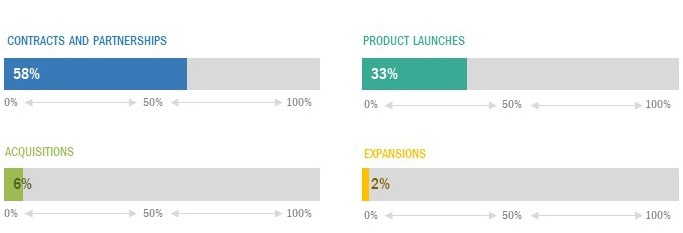
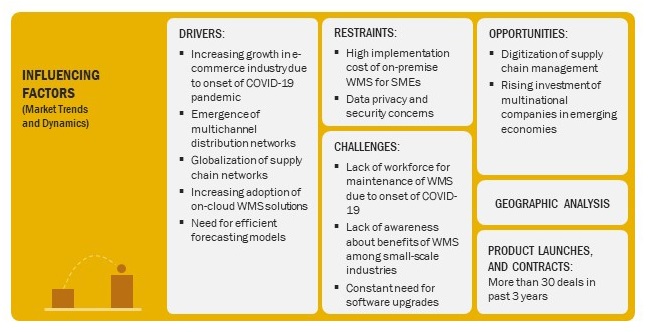
Major Drivers
Emergence of Multi Distribution Networks
A multichannel distribution network involves using more than a single channel for product distribution. In this highly competitive world, business owners have to come up with various strategies to expand their businesses. The primary driver for any business to grow is to increase their customer reach through various channels, including direct sales, online stores, franchise stores, and distributor sales. For example, a manufacturer can either sell products directly to its customers or through its own online stores, or through shopping websites, such as Amazon, BestBuy, and Alibaba. The advantages of using multichannel distribution networks include reaching customers through the easiest and relatable channel and providing customers with options for getting the best deal.
Globalization of Supply Chain Networks
Today, the manufacturing and warehousing facilities of businesses are spread worldwide. Companies managing supply chain networks across borders need to deal with regulatory and localization complexities. With the increasing number of facilities worldwide, sharing of information pertaining to products, suppliers, and workers has become a complex issue for warehouse operating companies. Multinational companies with global warehousing facilities are constantly looking for advanced solutions to instantly track their inventory. The dynamic nature of the global supply chain networks has increased the need for adaptable warehousing solutions. Moreover, the management of huge volumes of data generated from global supply chain operations poses a challenge for warehouse operating companies.
With the rise in international operations, product companies are using WMS solutions to plan, execute, and monitor the flow of goods across different geographies. Advanced WMS helps companies in streamlining their supply chain networks by providing an integrated platform for the efficient flow of data and information. By implementing WMS, companies can improve demand forecasting, make faster decisions, and process data pertaining to the movement of goods in a more efficient way.
Increasing Adoption of On Cloud WMS Solutions
An on-cloud WMS solution is an advanced version of WMS. Cloud computing is transforming the operational activities of a warehouse and supply chain management. Cloud-based WMS helps warehouse operators easily track inventory and ensure that the necessary stock is available to meet customer demands/orders. If there is any unpredicted demand for certain products, cloud computing makes it easier to respond quickly by communicating with suppliers and staff to get the required stock. Cloud-based WMS allows operators to remotely handle all their warehouse operations worldwide from a single location, thereby centralizing the control for better management. The ownership cost of an on-cloud WMS is lesser than the cost of setting up an on-premise WMS. On-cloud WMS even take lesser setup time than on-premise WMS. Thus, increased competitiveness, increased profitability, high scalability, and ease of use are some of the key factors driving the growth of the market for on-cloud WMS solutions.
Along with drivers, the below image presents all the market dynamics that have a profound impact on the warehouse management system market:
Warehouse Management System - By Components
The Warehouse Management System (WMS) integrates all equipment and activities in a warehouse to help manage the operations carried out within the warehouse. The introduction of indutry 4.0 and Internet of Things has led to the automation of most processes in warehouses, which makes use of robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRSs), cranes, and conveyors, and sortation systems. These automated material handling equipment are integrated with WMS software for the centralized management of various warehousing operations.
Robots
Traditionally, all activities in a warehouse were carried out by humans with the help of conventional material handling equipment. However, with the growing demand for automation, various operations are now carried out by robots. Initially, robots had limited capabilities and functionalities. However, with the development in robotic technology, the application areas of robots have increased across various industries. Robots can now assist in a number of warehouse activities, such as loading and unloading, sorting and picking, transporting, storing, and delivering. The use of robots aids in increasing efficiency, minimizing operational and logistics costs, and reducing delivery time. The use of robots is increasing in the warehousing sector owing to their high efficiency. The integration of robots with WMS allows to carry out designated activities smoothly. Currently, various robot manufacturing companies are making robots that can easily be integrated with WMS. Moreover, a few WMS software companies are developing software for easy integration with robots.
Automated Storage and Retrieval System (ASRS)
An automated storage and retrieval system (ASRS) is a system used to automatically store and retrieve materials from a defined storage location. These systems comprise four major parts: storage racks, input/output systems, storage and retrieval (S/R) equipment, and computer management systems. Some major automated functions performed by ASRS are unloading, sorting, storing, order picking, staging, and loading. These systems, based on their material handling capacity, can be categorized into unit load, mini load, carousel, shuttle, mid load, auto store, and goods-to-person. ASRSs are used to reduce the monotonous work of picking and placing of high volumes of inventory moving in and out of warehouses. These systems are also used in warehouse applications in which high storage density is required due to space constraints. Automated storage and retrieval systems were introduced in warehousing operations to automate labour-intensive and repetitive tasks. This is typically achieved by pairing ASRSs with WMS. WMS gives instructions to ASRSs about the exact locations of packages in an array of storage racks, as well as about volumes of inventory to be extracted. Once the ASRSs have picked or placed the items from the racks, the information gets updated in the central inventory database of the WMS. The integration of ASRSs with WMS enables warehouse operators to reduce errors, increase output, and efficiently manage storage and retrieval activities.
Conveyor and Sortation System
Conveyors and sortation systems are used to categorize and sort a mix of products on conveyor belts and send them to their correct locations, including shipping yards, pallets, and packing stations. In short, these systems track each product and divert it to its appropriate destination. Stationary or movable arms, pop-up wheels, rollers, or chains can be used as sorters to direct products to their desired destination. Conveyors and sortation systems reduce the need for human intervention, thereby increasing efficiency and accuracy. These systems also help in reducing product damages and increasing the overall throughput of warehouses.
Crane
Cranes are used to move and shuttle goods, materials, or products to and from warehousing facilities. These are used for handling materials that are heavy and require machines’ help to be transported from one place to another within a facility. Use of cranes aids in reducing labour costs, increasing efficiency, decreasing downtime, and increasing safety. These are primarily used in industries such as automotive, metals, and heavy machinery to handle heavy materials and smoothen processes. The types of cranes used in warehouses are bridge, jib, gantry, and stacker cranes. The integration of cranes with advanced WMS facilitates smooth operations at warehouses and superior control on the movement of goods from one location to another. Compared with manual operations of cranes, WMS helps warehouse-operating companies increase productivity, improve efficiency, and ensure the safety of warehouse personnel.
Automated Guided Vehicle
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are self-guided vehicles that can operate in complex material handling environments without any human intervention. AGVs can travel across floors by following guiding paths, such as markers or wires in the floors, or using vision, magnets, or lasers for navigation. These are used for applications that require consistent and predictable transport of materials. An AGV is an alternative to the transportation of goods using forklifts, trucks, conveyors, or manual carts, wherein a lot of human effort and other forms of energy are required. The use of AGVs decreases the load on humans to carry out non-decisive tasks—involving a lot of effort and time. Operations in warehouses include frequent transportation of goods from receiving stations to inventory racks, and from inventory racks to dispatch yards and docks. These operations are automated using AGVs, thereby ensuring safety and accuracy in material handling, along with lesser transportation time. Initially, the use of AGVs was limited to warehouses of manufacturing companies for transporting raw materials and finished goods within their facilities. However, with advancements in technologies and growing need for automation in industries such as 3PL, food & beverages, retail, e-commerce, and healthcare, the adoption of AGVs in distribution centres has increased. The integration of AGVs with WMS smoothens the transportation process within warehouses. AGV-integrated WMS solutions are available at exact locations in a given time to be loaded with the inventory, and these travel to correct yards or docks to be unloaded and dispatched. The entire process thus becomes highly automated and requires minimum human interference.
Warehouse Management System - By Offerings
Warehouse management systems are sold as per user requirements. Providers, based on their client requirements, integrate WMS with other equipment to best fit their warehouse operations. A WMS is generally offered with an after-sales service contract, which is periodically renewed or replaced by another WMS-providing company. The WMS market has been segmented by offering into software and services. The services segment has been further divided into consulting and installation, testing, maintenance, training, and software upgrades.
Software
The best Warehouse management system (WMS) is a software that manages the flow of inventory into, within, and out of a warehouse or multiple warehouses. The primary purpose of a WMS is to manage the overall activity within a warehouse and process associated transactions, including receiving, putaway, order selection, and shipping. A WMS also handles physical inventories, cycle counting, and the movement of materials from one location to another. This software ensures optimum utilization of resources and can be integrated with various material handling equipment, such as AGVs, robots, ASRSs, cranes, and conveyors and sortation systems, used in warehouses for smooth operations. The WMS software supervises and controls the flow of inventory in a warehouse through the receiving process. It then decides the location to place the inventory at the warehouse through slotting and putaway activities. The software is also responsible for managing the outflow of goods to proper shipping yards or docks.
Increasing demand for industrial IoT has resulted in the development of features and technologies associated with the WMS software. Advancements in warehouse management system software have resulted in a greater number of benefits, including increased optimization, reduced operational expenses, improved demand planning, better visibility of inventory, and enhanced labor productivity. Moreover, the integration of WMS software with other emerging technologies, such as ERP and CRM, has enhanced its capabilities.
Services
The WMS Solution is sold as a complete package, including a service contract, along with the software. Implementation of a WMS software alone does not meet the needs of a warehouse operator as it requires several services to ensure the smooth functioning of the software. WMS vendors sign high-value contracts with their customers to provide after-sales services. These services play a key role as they keep the systems optimized and ensure lesser production cycle time. The services offered by most WMS vendors include consulting and installation, testing, maintenance, training, and software upgrades.
Warehouse Management System - By Services
Consulting and Installation
Consulting services are provided before implementing WMS in warehousing facilities. In consulting services, vendors first understand their clients’ requirements and the current processes used to conduct daily warehousing operations; they then accordingly suggest the best modules of WMS. The vendors also solve customer queries on periodic or on a case-to-case basis after the WMS is operational.
After the consultation, the installation of WMS takes place. Installation is an important part of WMS services. Companies have the option to choose installation modes, such as on-premise or on-cloud deployment of WMS. Vendors perform the installation procedure very carefully as correct and precise installation of the software ensures the proper working of the WMS. On-premise installations are more time-consuming than on-cloud installations as vendors set up the software on companies’ internal networks, whereas cloud-based installations take place at vendors’ server networks.
Testing
Software testing is performed by WMS vendors at customers’ sites. This is done to ensure that the software is working as per the client requirements. Initial testing helps vendors detect faults and correct them before the software gets fully operational.
Maintenance
WMS software has to undergo periodic maintenance for proper functioning. Periodic maintenance helps in detecting malware or viruses affecting the software. It also helps in ensuring high-level performance of the WMS software to increase productivity, lower unwanted expenses, and reduce system breakdowns.
Training
Warehouse management system-related training covers WMS users’ interaction with mobile devices and software. Training involves key people on warehouse facilities, usually floor supervisors or warehouse managers, who use these systems. This training is provided by WMS vendors at the time of installation or at regular intervals to make warehouse operators aware of any changes made in the software and its operations.
Software Upgrades
Software upgrades are required to fix bugs and improve user experience. These upgrades help operators use the most advanced and competitive version of WMS, as well as help users ensure sustainable performance and prevent their software from unexpected shutdowns. Regular upgrades enable quick recovery of software in case of emergency.
Warehouse Management Systems - By Deployment
The Warehouse Management System market has been witnessing major developments for the past few years. Customers are demanding faster deployment of software, shorter processing times for their orders, and efficient warehouse operations at a low cost. Based on deployment, the WMS market has been segmented into on-premise and on-cloud. On-premise WMS is hosted on companies’ internal servers in warehouses; whereas, on-cloud WMS is hosted on servers maintained by cloud service providers and can be controlled from any remote location with the use of the Internet.
On-premise
On-premise WMS software is installed in on-premise servers to provide necessary computing power. It is basically set up at any location of a warehouse. Benefits offered by the on-premise Warehouse Management System include increased degree of control over the servers and software installed at the location, enhanced security, and improved performance. On-premise WMS solutions are less dependent on the Internet and can be customized easily. However, a high cost is associated with the implementation of on-premise WMS as operators have to own all the related hardware components, along with the licenses of support software required to power the WMS. Moreover, on-premise WMS adds a significant upfront cost in the form of dedicated IT personnel maintenances and periodic data backup performances. Despite the high cost associated with the deployment of on-premise WMS, it is still preferred by a large number of companies with warehouses owing to the benefits it offers, such as a higher level of data security and improved network performance. Companies involved in businesses that require a high level of data security for their products, materials, and inventory prefer on-premise WMS over on-cloud WMS. As the entire system is based on the premise of a warehouse facility, and there is limited use of internet connectivity, data remains secure at the warehouse location. Hence, companies opt for on-premise WMS installation to have a better control over data flow and sharing sensitive information.
On-cloud
On-cloud WMS software solutions are deployed or implemented using the Internet, and the unlimited computing power provided by server systems is maintained by cloud service providers. The on-cloud WMS software can be used at multiple locations, by many users, for processing large numbers of transactions simultaneously. This software is delivered either as a “one-size-fits-all” product or a uniquely configured solution accessible only by a particular customer. The customer pays a monthly or annual fee for the subscription of the software license, support, updates, and supplier’s infrastructure. Warehouse Management System software upgrades are easy as there is no need to visit various warehouse locations to upgrade software at customers’ servers. In this case, software providers control the delivery of the software using the Internet; hence, software upgrades are automatically available to customers. Some of the key advantages offered by on-cloud WMS are low-cost ownership, scalability, faster implementation, and lesser expense to maintain IT resources. Earlier, data security was the major concern preventing companies from adopting cloud-based WMS solutions. However, in recent times, this issue has been addressed by cloud service providers as they employ advanced security protocols and ensure periodic scanning of WMS software. This has created trust among warehouse operators to manage their warehousing activities through cloud-based WMS. Thus, the deployment of on-cloud WMS is gaining momentum and capturing a greater number of market shares of on-premise WMS.
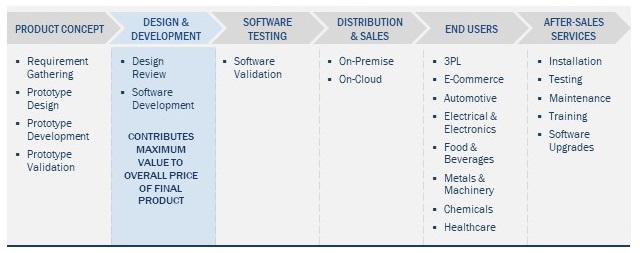
The below image shows further segmentation of the warehouse management system market based on various critical parameters:
What are the top 5 differences between On-premise WMS and On-cloud WMS?
|
Factors |
On-premise WMS |
On-cloud WMS |
|
Copyright |
Requires copyrighted software, which can be used only on a single machine or in one location |
Uses copyrighted software, but can be used across several hardware equipment or locations for a specific period based on the contract formed with WMS provider |
|
Customization |
Highly customizable as the entire system is self- owned and available on the premise |
Customizable under limited constraints as it has to be used for a number of applications and needs to comply with every location requirements |
|
Hardware |
Available on the premise |
Located at colocation center with the hosting provider |
|
Operating Software |
Available with hardware on the premise |
Available at colocation center and can be accessed through the Inter |
|
Upgrade activity |
Upgrade activities are planned by the internal IT department, and it is their responsibility to fix issues with the system |
WMS provider carries out periodic upgrade activities at a remote location |
What are the different tiers/levels of the Warehouse Management System?
Software companies offer flexible warehouse management solutions based on requirements and purchasing power of customers, and scale of operations. Warehouse management systems can either be simple or complex based on client requirements; WMS software can also be tailored as per customer needs. The cost of warehouse management systems depends on their features and functions. Based on features and functionalities, the warehouse management systems can be categorized into three tier types—advanced WMS (tier 1), intermediate WMS (tier 2), and basic WMS (tier 3).
Advanced Warehouse Management Systems – Tier 1
Advanced warehouse management systems, also known as tier 1 warehouse management systems, are considered an ideal software package for businesses that have highly complex operations; these WMS solutions offer the maximum number of features and functions. The implementation time of an advanced WMS is two or more years based on the system’s complexity. These are costlier than intermediate and basic warehouse management systems. However, the features and functions offered by these WMS solutions ensure efficient operations in warehouses, leading to higher productivity and larger profits. Industries such as consumer electronics, retail, and e-commerce that witness frequent product launches, comprise products with a short life cycle, and are dependent on seasonality factors can benefit from using tier 1 WMS solutions.
Intermediate Warehouse Management Systems – Tier 2
Intermediate warehouse management systems, also known as tier 2 WMSs, cover the functionalities and features of basic warehouse management systems and some added configurable functionalities. These systems cost lesser than advanced warehouse management systems and also offer lesser implementation time (3 to 6 months). Intermediate best warehouse management systems are generally preferred by small and midsized enterprises looking for high responsiveness and low maintenance costs. Tier 2 warehouse management systems also lack broader supply chain functions, such as transportation management and inventory planning. However, tier 2 WMS vendors have alliances with specific point solution providers to offer peripheral functionality to their customers. Key features of intermediate WMS solutions include high flexibility and adaptability, ease of integration, low cost, and focus on a particular industry.
Basic Warehouse Management Systems – Tier 3
Basic (tier 3) warehouse management systems cover only the necessary functions and features required for warehouse operations. These systems offer lesser features than advanced and intermediate warehouse management systems. However, these WMS solutions cost lesser than the other two WMS types and require 2 to 3 months for implementation. Basic warehouse management systems are ideal for applications in small-scale businesses that cannot afford high initial investments in WMS. This type of best Warehouse Management System involves a low level of integration with existing ERP systems in warehouses.
Features of a Warehouse Management System
A warehouse management system (WMS) incorporates several operations carried out in a warehouse for smooth functioning. WMS solutions provided by various vendors have different features and functionalities, and based on customer needs, the vendors offer WMS solutions integrated with required functions. Functions of WMS are vital for warehouse operating companies to ensure efficient movement of goods. WMS functions help manage and track all activities in a warehouse from receiving to shipment.
Receiving and Putaway
Receiving is one of the vital operations in a best warehouse management system. During this process, warehouse operators do not just collect goods but also transfer the ownership of the goods to themselves. Complete data about the goods or packages is then entered in warehouse management systems. This enables the systems to understand the content inside packages, their weight, dimensions, perishability, temperature, humidity requirements, and frequency or duration of stay at the warehouses. This data is vital for carrying out other supply chain activities. The receiving function involves scanning barcodes and QR codes or entering the data manually into the systems. The data collected during receiving operations by WMS is used to plan further operations at warehouses. Any inconsistency during data collection may affect the downstream workflow; hence, having optimum accuracy in receiving operations is mandatory. Putaway is the immediate step after receiving, in which a package is moved from the dock to the optimal storage location in a warehouse. The putaway function of a warehouse management system ensures that goods or packages are efficiently stored, distance to be travelled within the warehouse is minimum, security of goods is guaranteed, space at the warehouse is used optimally, and goods are easily accessible for retrieving during the picking process.
Customized Reporting
While typical reports are vital and are used through the whole supply chain process, a best warehouse management system should provide customized reports which can be saved and used, as well as organized, stored and shared electronically. Shipping documents should also be modified based on consumer requirements and be made available electronically.
Slotting
Slotting in a function of warehouse management systems that involves deciding an ideal place for every package or good in a warehouse based on its size, usage patterns, storage or pick types, environmental requirements, and customer base, among others. A warehouse management system considers all these parameters and looks for optimum floor space to place the goods.
Inventory Control
Inventory control helps in keeping track of inventory that is being brought in and sent out of a warehouse. The best Warehouse Management System software maintains a database of the inventory; this data is continuously updated with the flow of goods within the warehouse. The data is fed in inventory control of the warehouse management system from both receiving and dispatching ends of the warehouse. It keeps track of the inflow and outflow of goods, which helps in understanding the free capacity in the warehouse, availability of particular goods, and perishability timeframe of goods. The inventory data can also be fed in accounting and invoice systems, along with sales order processing and purchase order processing, to keep the inventory levels updated.
Picking
Picking is one of the most critical and time-consuming processes in a warehouse. It involves pulling out items from an inventory based on customer orders to be dispatched from the warehouse. This operation is carried out by a person or equipment available in the warehouse. WMS gives instructions to pickers or equipment about the exact location of the products, the quantity to be extracted, and the path to be followed for retrieving the items from inventory. These systems also provide additional details, such as rack numbers, levels, columns, and order in which the products are to be picked, to the pickers. These instructions facilitate optimum use of time and power to complete the task of picking. Picking operations in a warehouse account for ~55% of the total operational cost. An efficient and responsive picking process helps in significantly reducing operational costs, increasing profitability, and reducing instances of errors in picking up items and product returns.
Workforce and Task Management
Workforce and task management is considered to be a primary function of a warehouse management system. The workforce management function includes managing the number of workers that need to be active in a warehouse in a given time. It ensures that an optimum workforce is available at all times for carrying out tasks such as picking, receiving, and dispatching. This function also involves labor scheduling, staff forecasting, and leave management. Task management is a basic function for task allocation. Based on the demand for activities to be carried out, WMS allocates tasks to various workers and equipment. This function takes into consideration all the operations in a warehouse and accordingly allocates tasks to workers or equipment who/that can carry out the tasks without consuming much energy and time in transition. These decisions are made based on task priority and physical proximity of workers or equipment to task locations.
Shipping
The shipping function involves the maintenance of shipping documents and labels of shipment manifesting. It involves tracking the shipment of packages with unique codes until they are received by customers, or there are proofs of delivery. The function also involves the loading of packages in specific containers or trucks based on the importance, location, shape, and size of the packages. A WMS provides a proper list of items in a specific container or truck in a particular queue, thereby optimizing time, and loading and unloading efforts.
Yard and Dock Management
Yard and dock management is mostly an add-on function of warehouse management systems. This function is designed for larger and more complex warehouses, in which there are more than one dock points. It aids in integrating loading dock equipment with WMS to monitor, communicate, and manage loading dock status. The yard and dock management function allows operators to manage the flow of goods to the right docks and avoid any misplacement of shipment packages. It also helps them plan the arrival and departure of containers and trucks at certain docks or yards to avoid bottlenecking of more than one transport vehicle. Most yard management modules offer basic radio-frequency (RF) direction of workers’ activities; some also support radio-frequency identification (RFID) tagging of vehicles and containers, allowing warehouse operators to track vehicle and container movements in real time.
This is how a modern day Warehouse Management Value Chain functions:
Current Trends in the Warehouse Management System Market
Warehouse Robotics - Companies have been accepting warehouse robotics, which are backed by latest technology and they enable businesses to reduce their labour costs, enhance workflows and increase the bottom line.
Cobotics - Warehouse robots can operate self-sufficiently as well as next to and in collaboration with their human counterparts. Cobotics refers to merging some of the key competences of robots such as accuracy, speed and repeatability, with people-specific skills such as knowledge, analysis and decision making.
Wireless Fleet Management – One way IoT is transforming the world of warehousing is through wireless fleet management. It is a latest technology that leverages sensors to precisely track each truck in the fleet in real time through an online portal.
This is how a modern day